Corneal Flap Lasik
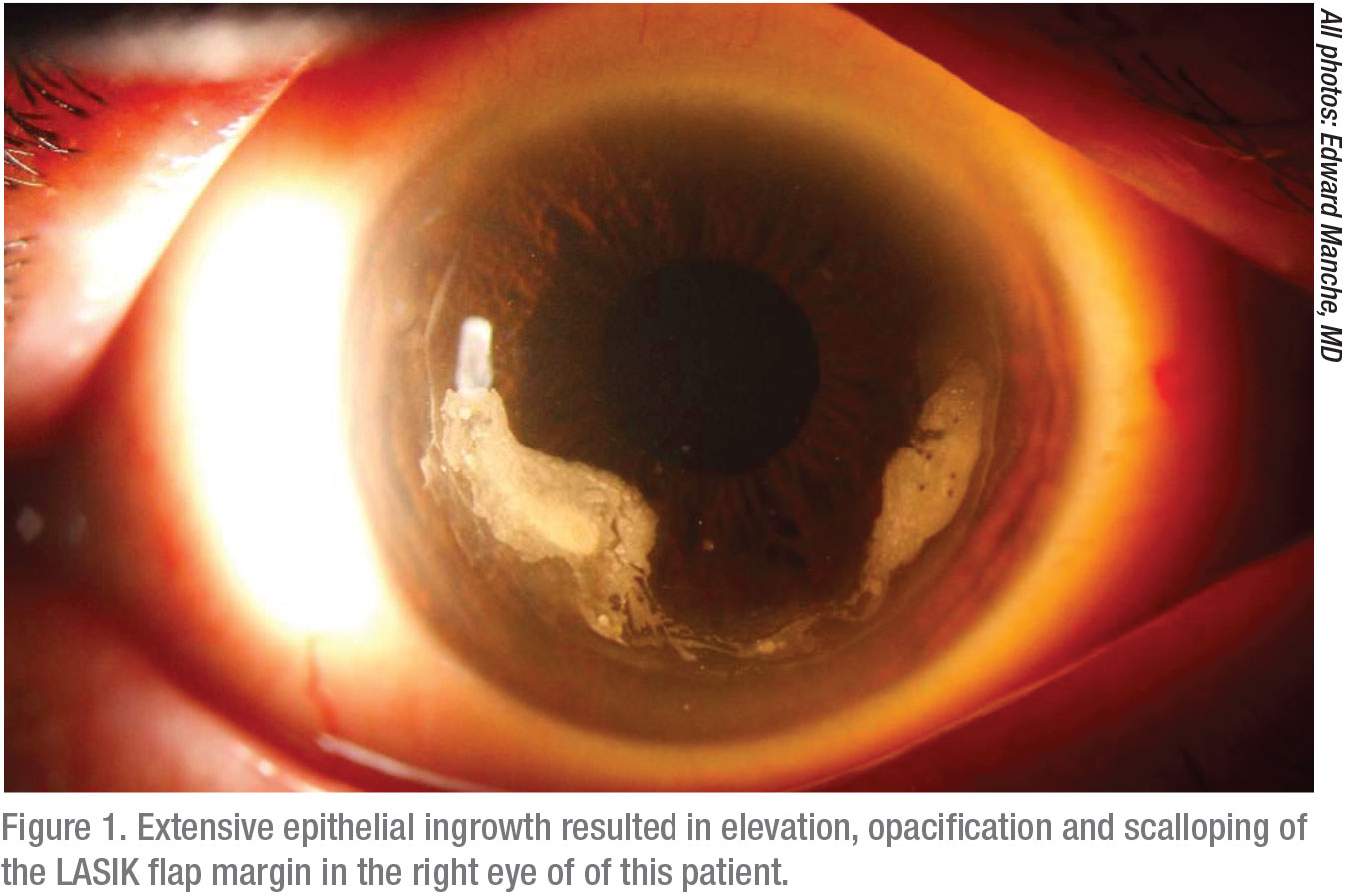
/ectasia_flap_margin(425).jpg)
Lasik Flap Dislocation The Flap Never Heals

Lasik Flap Stability After Severe Ocular Injury Sciencedirect

Best Eye Hospital In Indore Best Eye Hospitals In Indore Best Eye Clinics In Indore Best Hospital Near

Flap Striae Columbia Ophthalmology

Lasik Eye Surgery For Vision Correction At Fort Worth Eye Associates

Post Lasik Granular Corneal Dystrophy
Both LASIK and PRK use a laser to reshape the cornea, the clear outer layer of your eye that focuses light so you can see clearly But they do it in slightly different ways LASIK creates a thin.
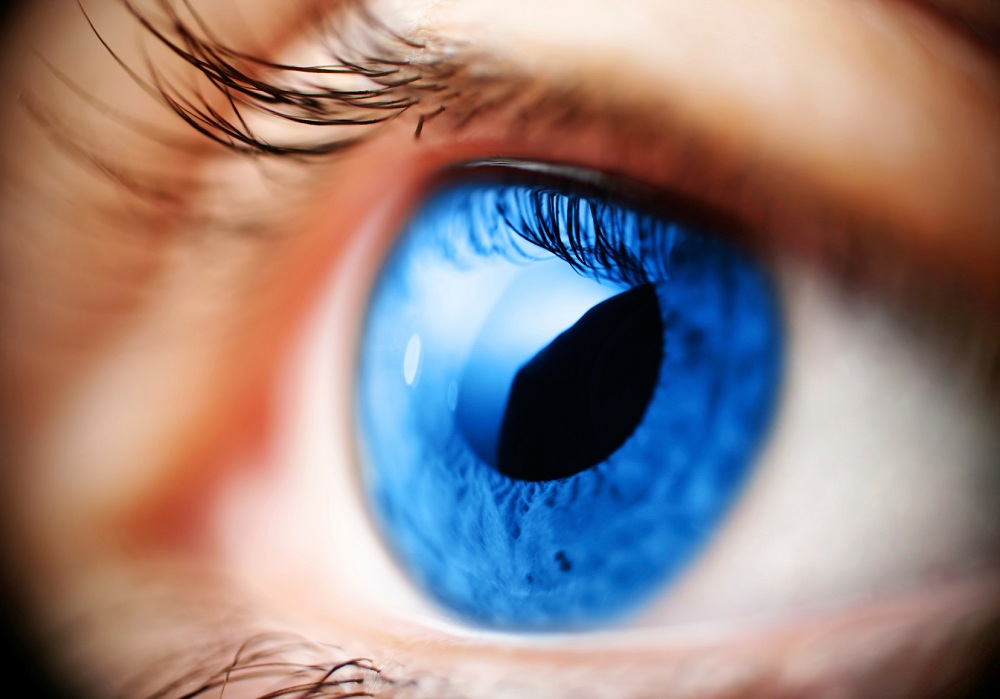

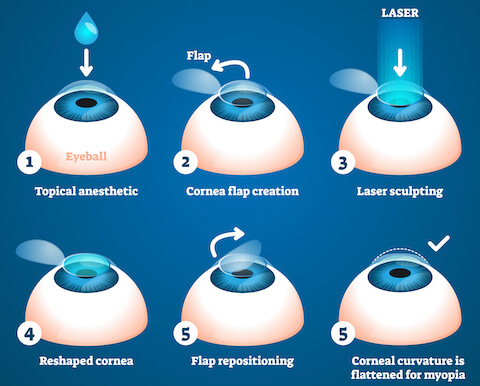
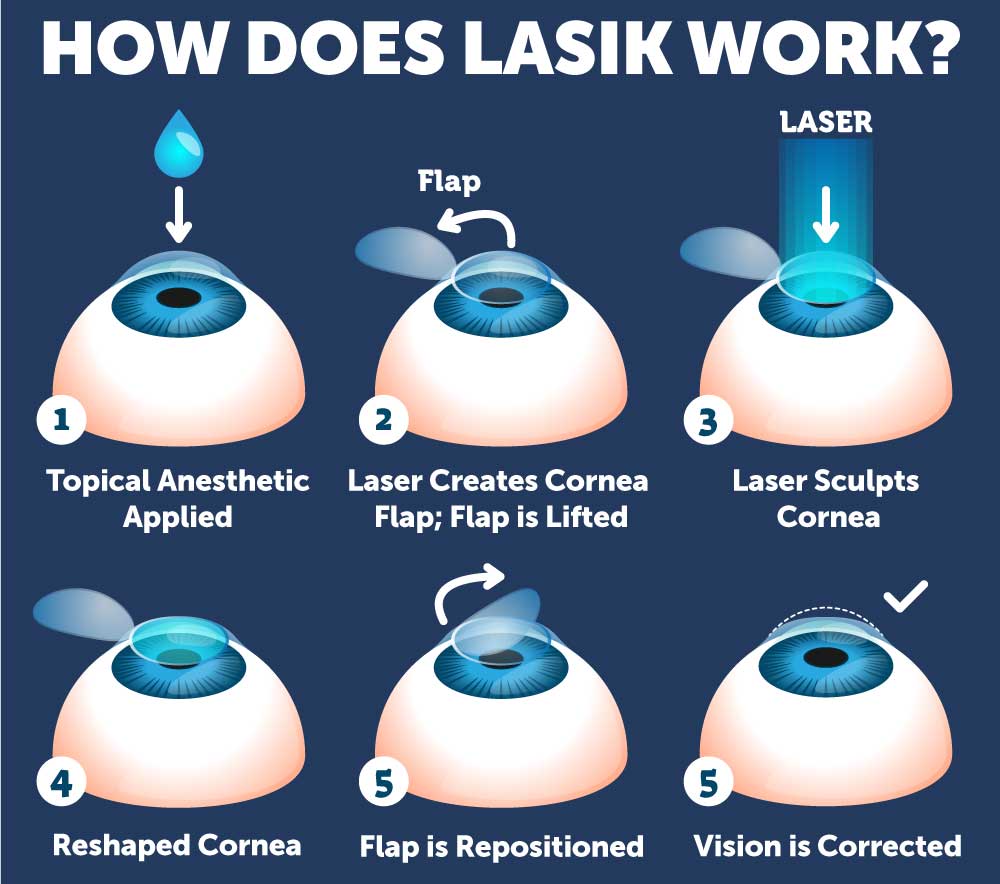
Corneal flap lasik. LASIK, which stands for laserassisted in situ keratomileusis, is a type of refractive surgery The surgeon first cuts a thin flap of tissue from the front of the eye Then, a laser burns away. When considering other complications of LASIK flaps, one of the most common is a ‘flap striae’, which is simply small wrinkles or folds in the cornea as a result of LASIK surgery While this LASIK side effect is not uncommon, it is also asymptomatic for the vast majority of cases and only detectable with a microscopic examination. At the start of your LASIK surgery, an eye surgeon will use a femtosecond laser to create a flap on the surface layer of the cornea This laser is computerguided, allowing the surgeon to produce the flap with a perfectly precise circular incision around the outer corneal tissue that is catered to the specific eye shape.
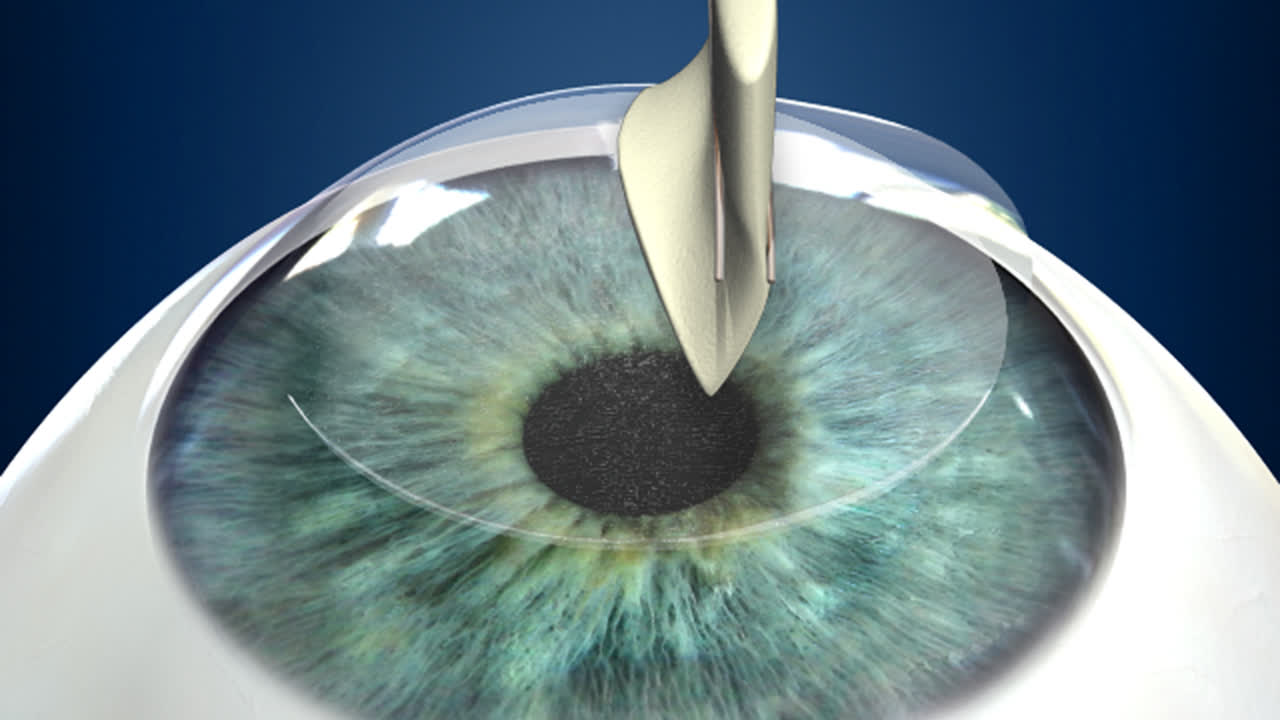
During LASIK surgery, a flap incision is created in the outer, epithelial, layer of the cornea With the flap open, the surgeon can then reshape the stromal layers of the cornea to achieve the precise shape upon which light can directly reflect off the retina and produce clear vision Why Is Corneal Thickness Important?. ILASIK combines the accuracy of the Excimer laser with the quick healing characteristics of a Femtosecond created flap Using a Femtosecond laser, a thin, protective flap of corneal tissue, attached by a hinge on one side, is folded back so the inner tissue of the cornea (stroma) can be treated with the excimer laser. Creating the Corneal Flap To create the corneal LASIK flap, the LASIK surgeon uses a handheld device or a laser to cut the top layers of corneal tissue at a predetermined depth One edge of the flap is left uncut, forming a hinge Using the hinge, the surgeon folds back the flap to access the underlying corneal tissue After the surgeon has.
Flap striae are defined as small wrinkles or folds in the cornea as a result of LASIK surgery Classification The most common classification of flap striae divides them broadly based on their size Microstriae are microscopic, superficial wrinkles that are generally asymptomatic and often only detectable on microscopic examination of the cornea. In addition, a new study from our center suggests that flaps created using the femtosecond laser result in smaller, more consistent, and more predictable changes in corneal biomechanics compared with flaps created using a mechanical microkeratome 18 This potential additional advantage may turn out to be the most important of all Developing technology that reduces the risk of postLASIK ectasia is the most important priority in refractive surgery today. LASIK (laser in situ keratomileusis) is a surgical procedure designed to correct refractive errors LASIK involves creating a corneal flap using a microkeratome or a femtosecond laser, reshaping the cornea using an excimer laser to remove tissue from the underlying stromal bed and then replacing the flap Figure 1 Lifting of LASIK flap.
The cornea is incapable of complete healing after LASIK The cornea forms a miniscule scar at the edge of the LASIK flap, which holds the flap in place, but the flap itself does not bond to the underlying cornea Medical research has repeatedly demonstrated that the LASIK flap never heals. LASIK Flap Buttonhole Disease Flap buttonholes are caused by an abnormal lamellar cut during the creation of the LASIK flap where there is a connection between the flap interface and the corneal surface Etiology Flap buttonholes are caused by an abnormal lamellar cut during LASIK flap creation with either microkeratome or a femtosecond laser. During LASIK, a small flap is created in the topmost layer of the corneal, which is known as the epithelium By moving this top layer of the cornea back, a LASIK surgeon can then reshape and recontour the corneal surface and improve the passage of light through the eye Once the corneal reshaping is commplete, the flap is set back down.
Corneal infection can occur after lasik surgery and can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus and acanthamoeba The symptoms are red eye, pain, discharge and blurred vision Treatment is with antibiotics and sometimes with flap lifting and irrigation with sterile fluid and antibiotics 6 Epithelial Ingrowth. ILASIK combines the accuracy of the Excimer laser with the quick healing characteristics of a Femtosecond created flap Using a Femtosecond laser, a thin, protective flap of corneal tissue, attached by a hinge on one side, is folded back so the inner tissue of the cornea (stroma) can be treated with the excimer laser. The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap.
Alright, so how does the corneal flap heal after LASIK?. There are two steps of LASIK 1 Creation of a corneal flap to allow access to your underlying corneal tissue This is performed using the IntraLase femtosecond laser to create a precise, smooth flap in the safest manner possible 2 Corneal reshaping using Wavefront VISX CustomVue technology Only a miniscule amount of corneal tissue is gently. There are two steps of LASIK 1 Creation of a corneal flap to allow access to your underlying corneal tissue This is performed using the IntraLase femtosecond laser to create a precise, smooth flap in the safest manner possible 2 Corneal reshaping using Wavefront VISX CustomVue technology Only a miniscule amount of corneal tissue is gently.
Purpose To describe the morphological characteristics of microfolds that appear at the corneal flap after LASIK, as seen under confocal microscopy Methods Twentyone eyes that had undergone LASIK were examined, all within 3 weeks to 1 month after surgery A central scan of the total corneal thickness was obtained by using confocal microscopy in vivo. Moreover, excessive flap manipulation may produce an irregular flap and cause corneal striae Mechanical trauma after LASIK can dislocate the flap and result in striae This trauma can be minimal, caused by eye rubbing or eye squeezing Although dry eye does not cause striae, an epithelial defect resulting from the condition can. In addition, a new study from our center suggests that flaps created using the femtosecond laser result in smaller, more consistent, and more predictable changes in corneal biomechanics compared with flaps created using a mechanical microkeratome 18 This potential additional advantage may turn out to be the most important of all Developing technology that reduces the risk of postLASIK ectasia is the most important priority in refractive surgery today.
The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap. LASIK works by removing (ablating) tissue from the cornea This reshapes the surface of the cornea to correct the refractive error The amount of corneal tissue that is removed from the stroma is call the ablation depth, and this depends on the degree of refractive error. Intraoperative Complications Microkeratomerelated flap complications Other risk factors include loss of suction, defective blade, abnormal Corneal Epithelial Defect The risk factors of epithelial erosion during LASIK include older age, previous corneal Limbal Bleeding It occurs in two.
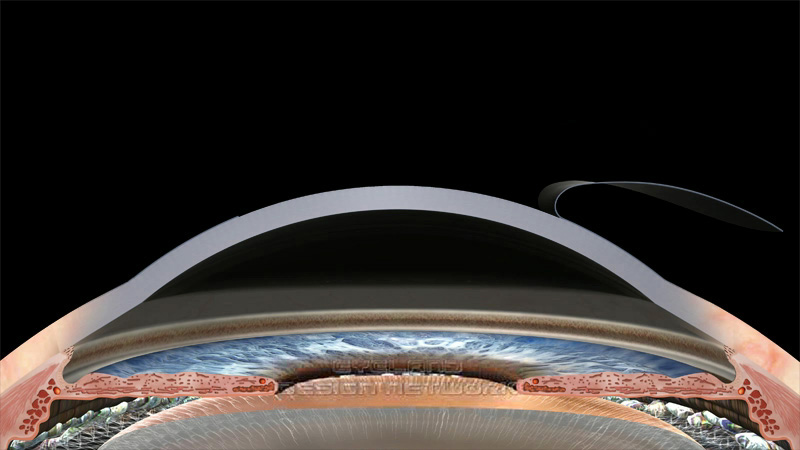
The corneal flap heals in different ways at different parts of the flap We’ve broken it down for you here Epithelial layer Your epithelium is the very, very thin layer found on the surface of the cornea It begins healing almost immediately after the flap has been replaced and is the. LASIK surgery involves two basic steps creating a corneal flap and reshaping the cornea according to prescription Traditionally, the corneal flap during LASIK has been created with a microkeratome blade It is well documented that a large part of the risks and complications from LASIK arise during the creation of the flap. Laserassisted in situ Keratomileusis (LASIK) The surgeon uses either a microkeratome or a femtosecond laser to cut a flap of the corneal tissue (usually with a thickness of 100–180 micrometres) The flap is lifted like a hinged door, but in contrast to ALK, the targeted tissue is removed from the corneal stroma with an excimer laser The flap is subsequently replaced.
Under his guidance the Swiss laser maker Zeimer has developed the technology to create LASIK flaps of 90 or 100 microns — or less than 1/10th of a millimeter!. How Does Lasik Work?. During LASIK surgery, a flap incision is created in the outer, epithelial, layer of the cornea With the flap open, the surgeon can then reshape the stromal layers of the cornea to achieve the precise shape upon which light can directly reflect off the retina and produce clear vision Why Is Corneal Thickness Important?.
The corneal flap is constantly observed throughout the lasik procedure The flap does not dislocate as the very edge is not cut through (making it a flap) The surgeon smooths the corneal flap down after the correction is completed It then adheres and heals in a short amount of time. Although the biomechanical mechanisms for creating the flap in LASIK refractive surgery had been studied, FEM relied strongly on the mechanical properties that were assigned to the corneal tissue and some assumptions within the model. The creation of a flap in the outermost layer of the cornea is what distinguishes LASIK from other forms of laser refractive surgery, such as PRK and LASEK This means that flap complications are a potential risk of all forms of LASIK.
Corneal transplant LASIK permanently thins and thereby weakens the cornea This can lead to the need for a cornea transplant, despite a LASIK surgery being deemed “successful” Corneal flap dislocation The corneal flap is altered during every LASIK surgery However, in some cases, this eventually leads to a dislocated corneal flap. Laser Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis (LASIK) flap complications occur more frequently in the early postoperative period 1 However, traumatic dislocations have occurred up to 14 years after the procedure 2 On the other hand, total avulsion of the LASIK corneal flap (sometimes with flap loss) is much less common. Alright, so how does the corneal flap heal after LASIK?.
How the flap is made during laser eye surgery When laser eye surgery was approved by the FDA for use in 19, the surgeon would use a microkeratome – a surgical instrument with an oscillating blade – to precisely create the corneal flap In 01, the femtosecond laser was approved for use in laser eye surgery This laser performs a perfect incision by using ultrashort pulses. As a result, there is no way for the flap to remain Buttonhold flaps – occur when the flap is too thin;. The emergence of femtosecond laser technology has revolutionized lamellar flap creation The refractive surgery community continues to debate whether to use either a blade or laser to create corneal flaps This article discusses the clinical advantages and disadvantages of the femtosecond laser and mechanical microkeratome for LASIK flap creation.
Corneal abrasions are typically caused by the microkeratome (surgical blade) used to create the corneal flap during LASIK surgery In some cases they heal on their own Treatment Application of a contact lens, which serves as a bandage to protect the healing cornea. The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap. ILASIK combines the accuracy of the Excimer laser with the quick healing characteristics of a Femtosecond created flap Using a Femtosecond laser, a thin, protective flap of corneal tissue, attached by a hinge on one side, is folded back so the inner tissue of the cornea (stroma) can be treated with the excimer laser.
A hole appears in the middle of the flap Incomplete flaps. Abstract Worldwide, femtosecond Laser Assisted Insitu Keratomileusis (LASIK) is a well known and commonly used refractive technique, although Small Incision Lenticule Extraction (SMILE) has become increasingly popular since it was introduced in 11 In LASIK, a corneal flap is cut with a microkeratome or femtosecond laser, followed by thinning of the stromal bed with excimer laser ablation. The corneal flap heals in different ways at different parts of the flap We’ve broken it down for you here Epithelial layer Your epithelium is the very, very thin layer found on the surface of the cornea It begins healing almost immediately after the flap has been replaced and is the reason that you don’t feel a “line” between the flap and the rest of your eye.
Then the LASIK flap was repositioned and the cornea was continuously illuminated for 130 minutes with 30 mW/cm 2 using a KXL ultraviolet light source (Avedro Inc) delivering an energy dose of 2. Complications relating to the corneal flap created during LASIK include Free caps – occur when no hinge is made during flap creation;. Once the computerassisted laser has treated the inner part of the eye, the corneal flap is replaced and starts to heal As soon as the flap is placed back to its natural position, negative suction immediately binds the tissue to the surface of the eye.
During LASIK eye surgery, the surgeon first administers numbing drops, which take effect in 1015 minutes, and then creates a thin, corneal flap with the laser The surgeon then pulls back the flap to expose the underlying tissue and reshapes the stroma layer of the cornea Then, the laser removes cells according to your prescription. Corneal transplant LASIK permanently thins and thereby weakens the cornea This can lead to the need for a cornea transplant, despite a LASIK surgery being deemed “successful” Corneal flap dislocation The corneal flap is altered during every LASIK surgery However, in some cases, this eventually leads to a dislocated corneal flap. During LASIK surgery, a small flap is created in the frontal, topmost layer of the cornea This layer is called the epithelium Using this epithelial flap, the cornea can be reshaped and recontoured as needed to address refractive errors (ie, myopia/nearsightedness, hyperopia/farsightedness, and astigmatism).
The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap Over the next few weeks, natural substances inside your cornea bond the corneal flap to the underlying tissue. The vision in the left eye, which had been left a little myopic by the monovision LASIK, was /50 uncorrected, and /1 with correction Upon examination, Dr McCabe saw that the left eye’s flap was torn, and there was epithelial ingrowth, fixed folds and anterior stromal scarring. February 4, 15 by Andrew Caster Myth A common concern about Lasik surgery is that the corneal flap will never heal To break it down quite simplygive it some time In the early days after Lasik, wounds should be handled with great care because that’s when the eye is most vulnerable and susceptible to trauma.
Instead of completely removing a section of the cornea, LASIK technicians use a specially formulated tool to gently fold a sliver of the cornea back This flap stays connected throughout the procedure What Happens Next?. The Ziemer femtosecond laser uses a low energy laser to make small bubbles at a precise depth in the cornea. The LASIK flap heals back into its original position and the healing process is not limited to he edge alone The healed flap is stable and unlikely to dislodge with eye rubbing Significant eye trauma could potentially dislocate the flap, however, such instances are rare Flap creation making use of the femtosecond laser provides for even greater stability and reduced chances of flap movement or dislocation.
During LASIK surgery, a small flap is created in the frontal, topmost layer of the cornea This layer is called the epithelium Using this epithelial flap, the cornea can be reshaped and recontoured as needed to address refractive errors (ie, myopia/nearsightedness, hyperopia/farsightedness, and astigmatism). Methods Twentyone eyes that had undergone LASIK were examined, all within 3 weeks to 1 month after surgery A central scan of the total corneal thickness was obtained by using confocal microscopy in vivo Confocal images were captured and digitized. How Does Lasik Work?.
The first step in the LASIK procedure is creating a corneal flap This is usually performed with a surgical tool called a microkeratome or a laser called IntraLase A ring is placed on the surface of the cornea and is held in place with suction. How Does Lasik Work?. The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap Over the next few weeks, natural substances inside your cornea bond the corneal flap to the underlying tissue.
A 54yearold man had undergone uneventful LASIK (nasal hinged flap using an Automated Corneal Shaper microkeratome with a 160 microns plate) in both eyes (OU) in 01 for the correction of composed myopic astigmatism. The LASIK flap heals back into its original position and the healing process is not limited to he edge alone The healed flap is stable and unlikely to dislodge with eye rubbing Significant eye trauma could potentially dislocate the flap, however, such instances are rare. The main difference between PRK and LASIK is that in LASIK surgery a thin, hinged flap is created on the cornea to access the treatment area, whereas in PRK the cornea’s entire epithelial (outer) layer is removed to expose the area and no flap is created For both PRK and LASIK, the excimer laser then sculpts the stromal layer of the cornea to correct your refractive error.
The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap. LASIK may lead to a decrease in structural stability of the cornea in some circumstances6 By making a LASIK flap and removing tissue, the anterior layers of the corneal structure are modified and, hence, corneal rigidity may decrease According to John Marshall, PhD, LASIK may weaken the cornea by 15% to. There are two steps of LASIK 1 Creation of a corneal flap to allow access to your underlying corneal tissue This is performed using the IntraLase femtosecond laser to create a precise, smooth flap in the safest manner possible 2 Corneal reshaping using Wavefront VISX CustomVue technology Only a miniscule amount of corneal tissue is gently.
The corneal flap begins healing immediately after the LASIK procedure In fact, with the use of a LASIK flap, the corneal tissue can be as much as 90% healed within 24 hours During the first day or two after surgery, the outer surface of the cornea, known as the epithelium, seals the edges of the corneal flap. Eye surgeons report that the flap created on the surface of the cornea is often the main source of vision problems following LASIK surgery Though these complications are rare, healing problems, scarring, or unhealed and unsecured corneal flaps are often what cause poor LASIK outcomes Surgeons report that microkeratome flaps might lead to.
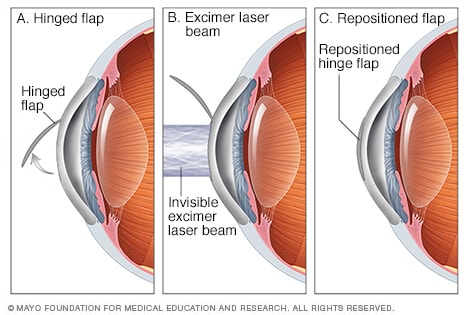
Lasik Eye Surgery Mayo Clinic
.jpg)
Lasik Flap Dislocation The Flap Never Heals
/detached-lasik-flap(640).jpg)
Lasik Flap Dislocation The Flap Never Heals

Lasik Enhancement With Epithelial Cells Growing Under Flap Youtube

Clinical Case With Post Lasik Ectasia Due To A Thick Corneal Flap A Download Scientific Diagram

Full Text Traumatic Corneal Flap Displacement After Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Imcrj
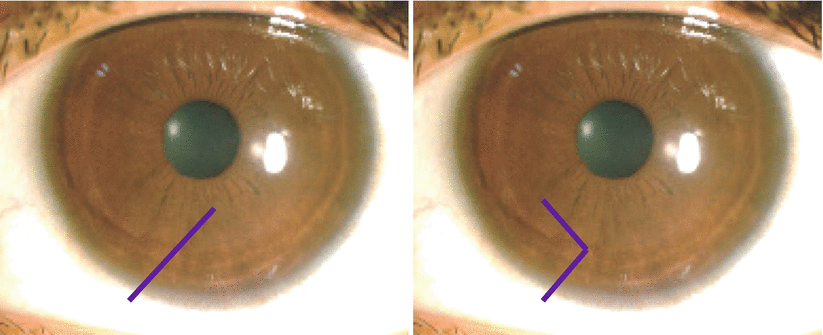
Intraoperative Flap Complications In Lasik Prevention And Management Of Free Flaps Springerlink
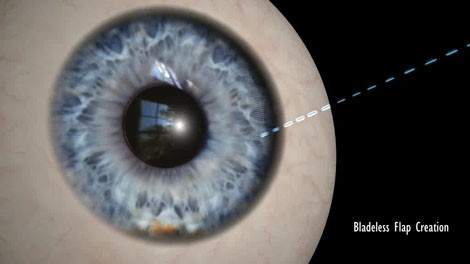
Z Lasik How Bladeless Eye Surgery Works

Lasek Eye Surgery A Better Choice Than Lasik Allaboutvision Com
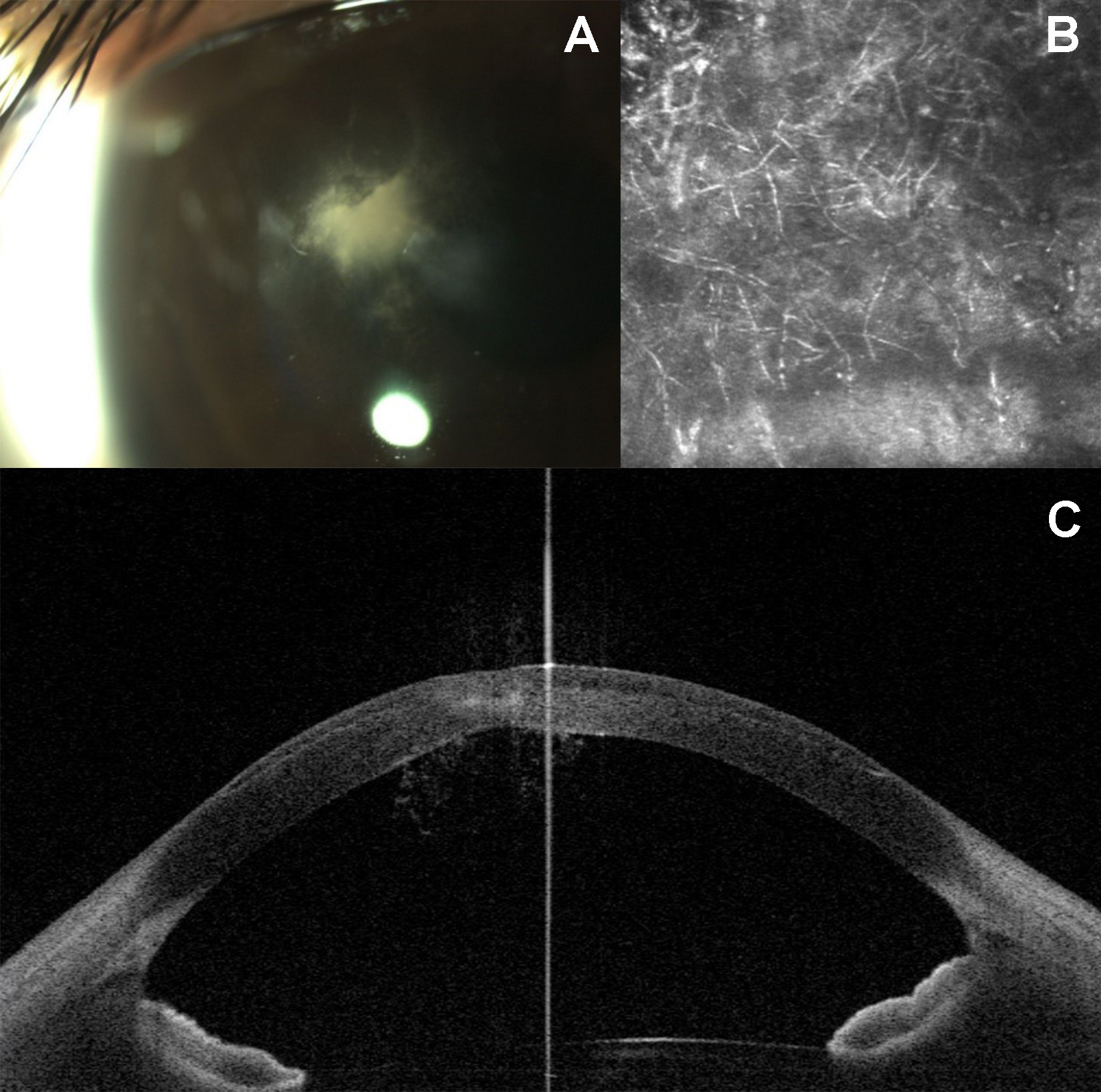
Millennialeye Post Lasik Fungal Flap Infection

Early Post Lasik Flap Amputation In The Treatment Of Aggressive Branching Keratitis A Case Report

Lasik Surgery Explained Definition Procedure Results

How Does Cornea Thickness Affect My Candidacy For Lasik Price Vision Group

Lasik Laser Eye Surgery Fairfield Meriden New Haven Stamford Ct

Eye에 있는 핀
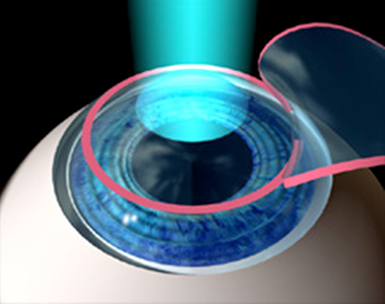
Prk Vs Lasik Eye Care Associates

Lasik Understanding Lasik The Vision Correction Website
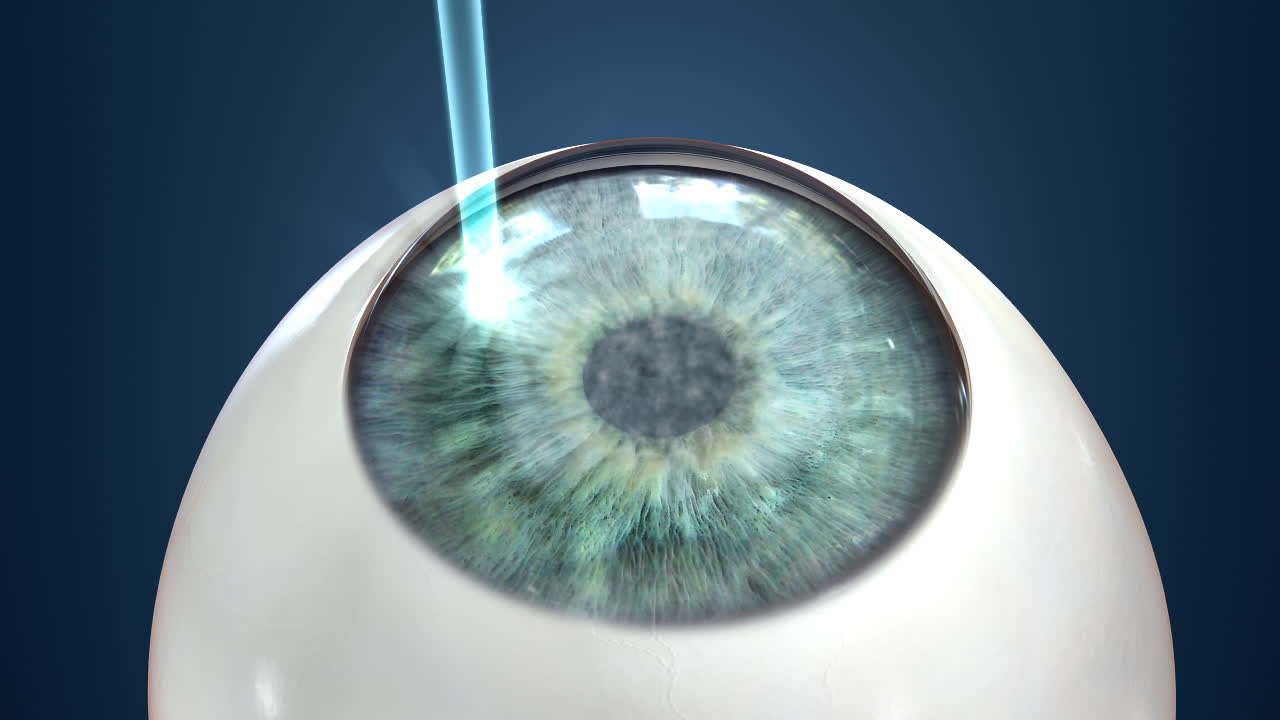
Bladeless Intralase Flap Miami Laser Eye Surgeons Tlc Of Coral Gables

Lasik Long Beach Leading Lasik Surgeons Socal Eye

Lasik Prk Grosinger Spigelman Grey
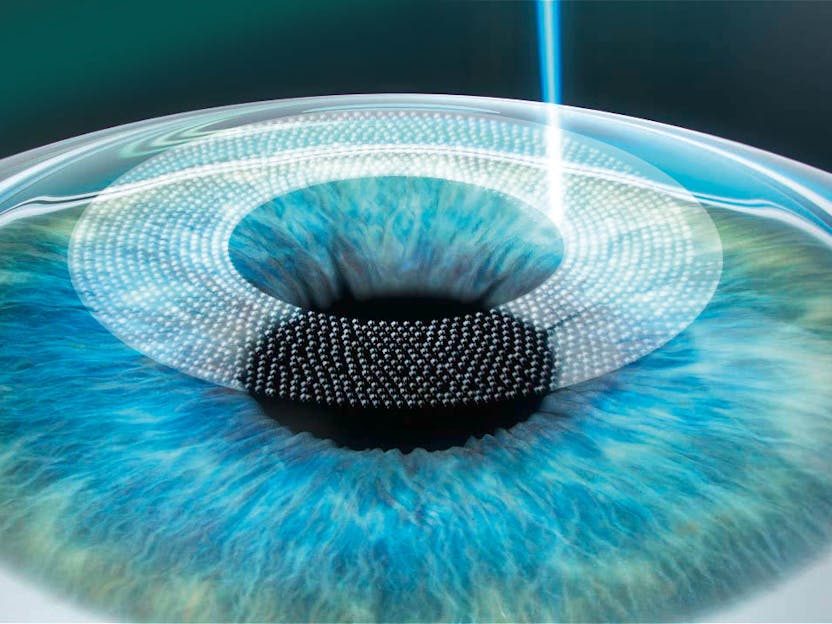
Lasik Laser Eye Surgery

Lasik Prk Grosinger Spigelman Grey
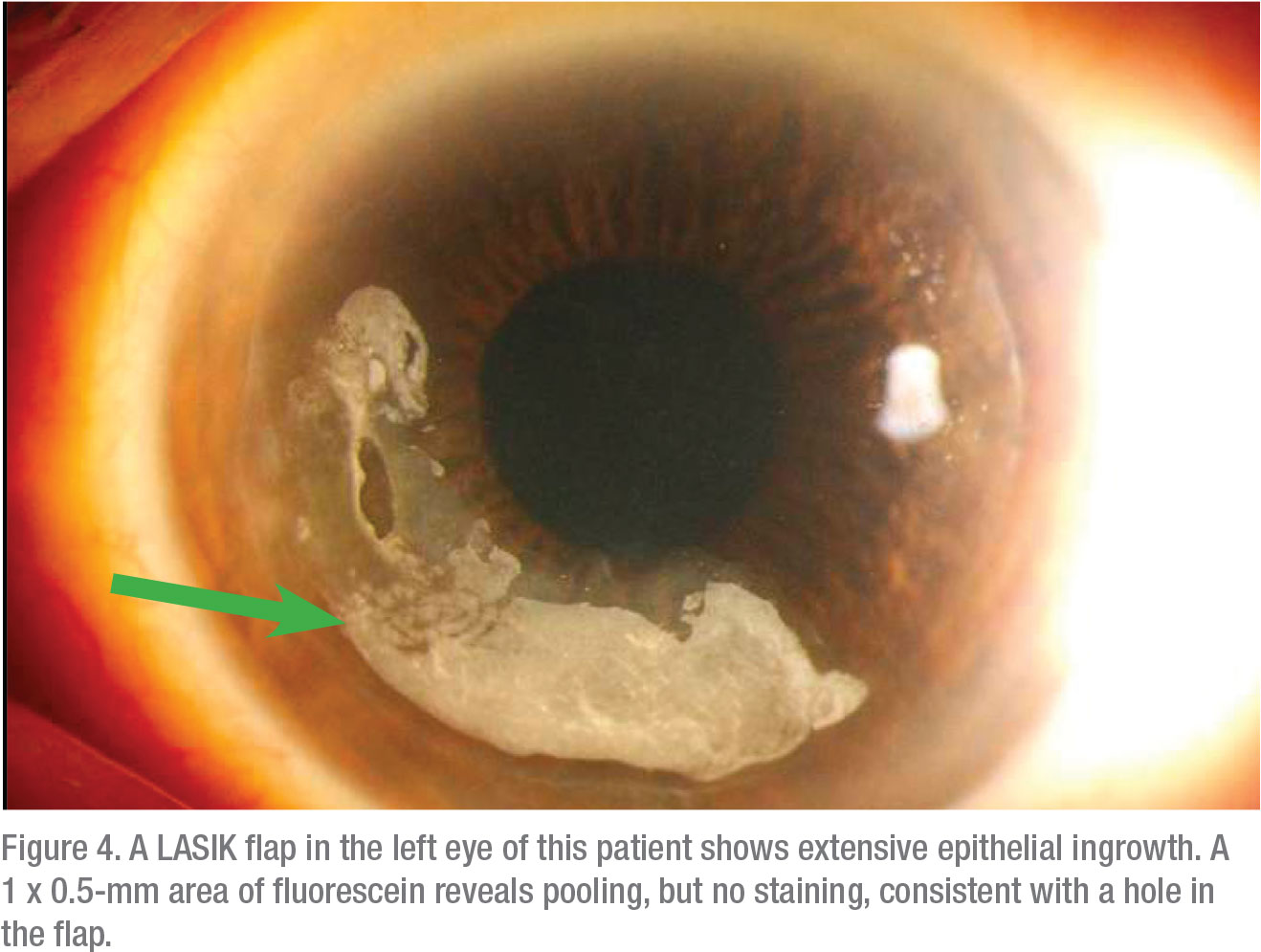
Before Enhancing Post Lasik Patients
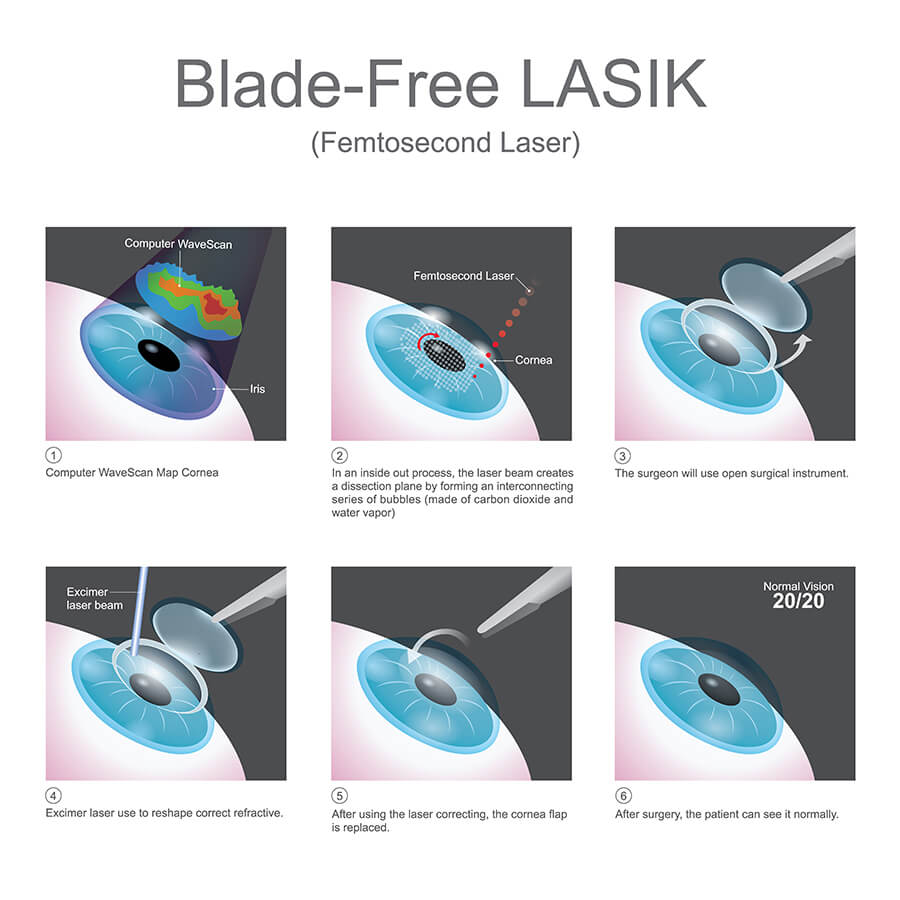
Lasik Eye Surgery Los Angeles Laser Vision Medical Associates

Lasik Wikipedia

Eyeworld Management Of Rare Post Lasik Complications

The Para Position Of The Corneal Flap In The Left Eye Is Satisfactory 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Lasik Photo Gallery Sclerallens Com
Replacing My Corneal Flap During Lasik Surgery Interestingasfuck

Fifteen Months After Flap Suturing The Stable Lasik Flap Is Held In Download Scientific Diagram
Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Lasik American Academy Of Ophthalmology
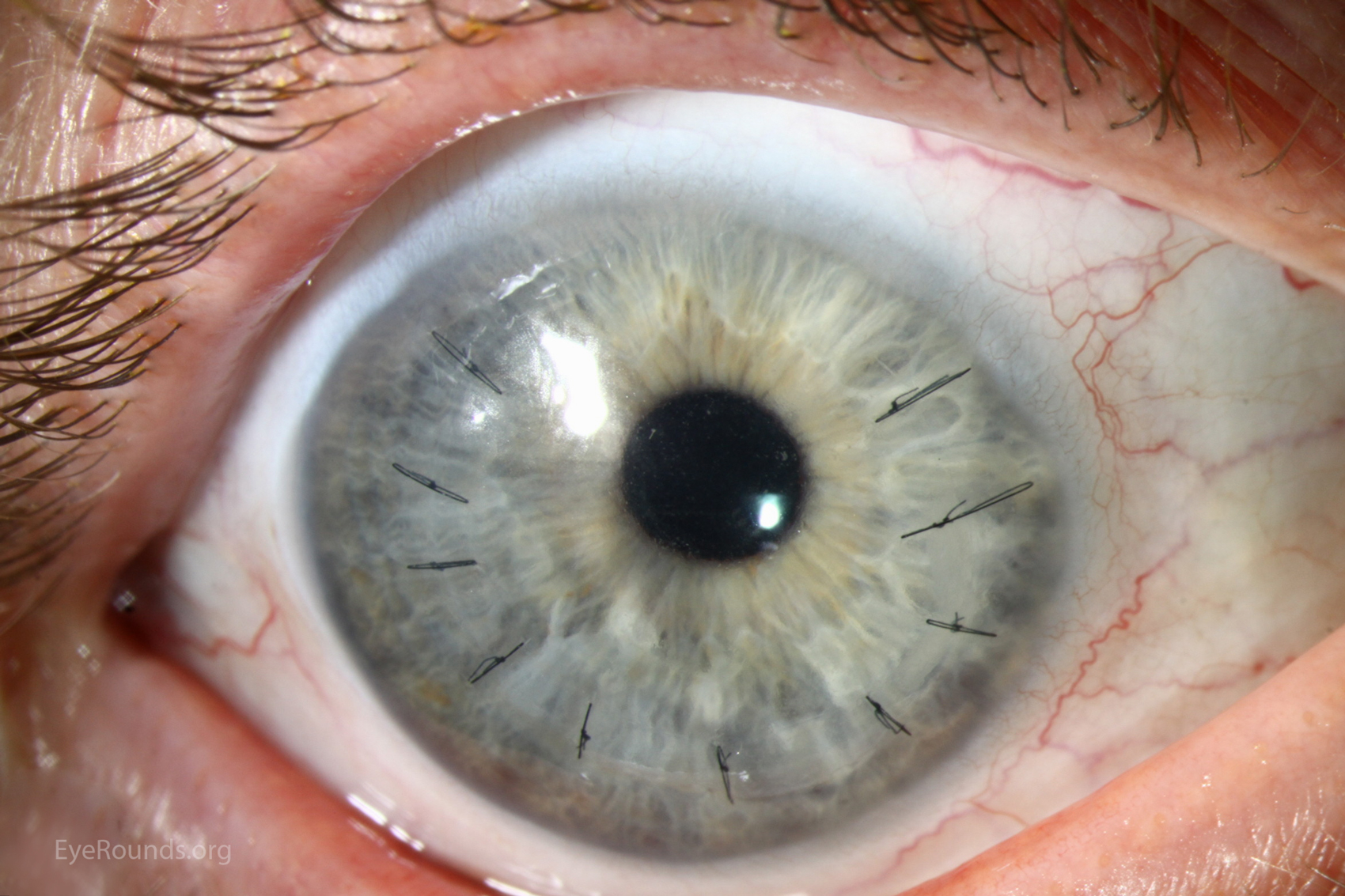
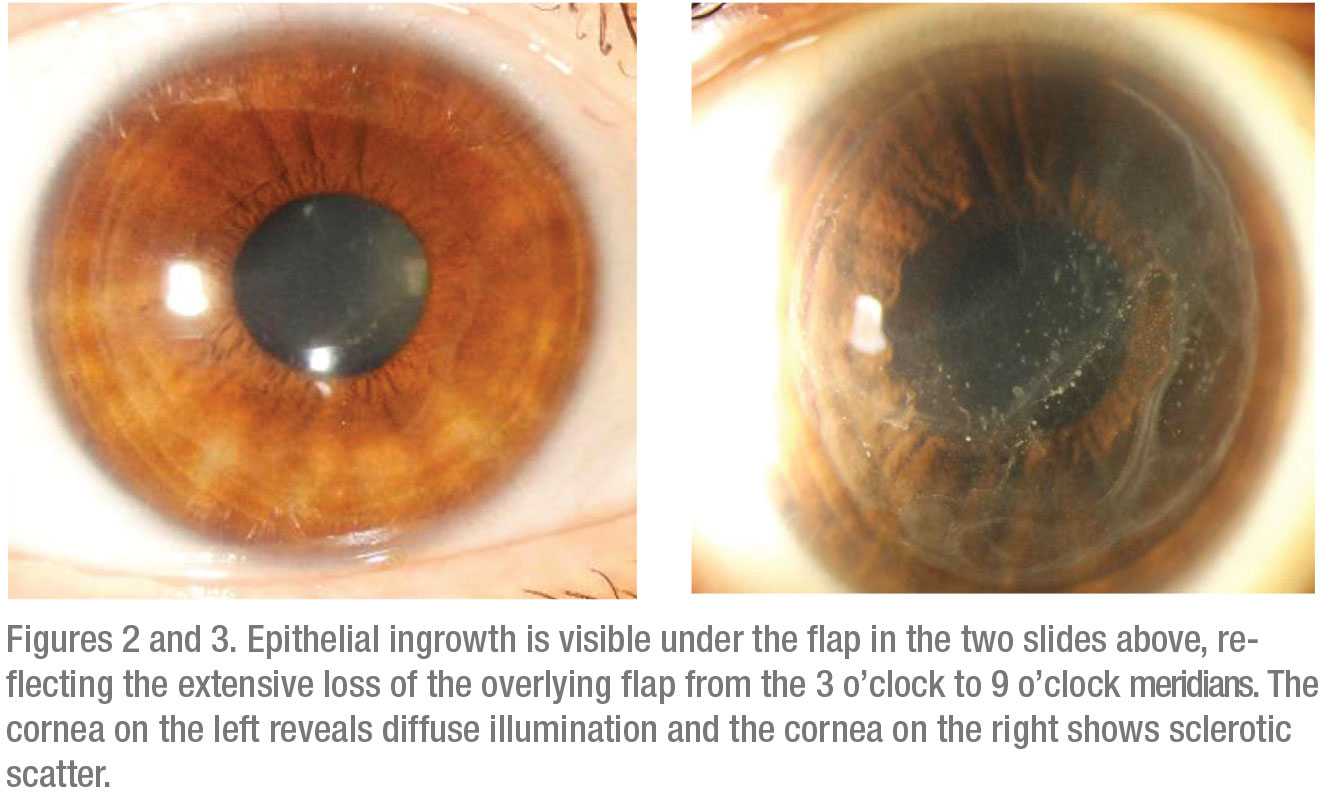
Epithelial Ingrowth Under Lasik Flap

What Can Go Wrong Lasik Surgery The Eye Clinic Surgicenter Billings Eye Clinic Surgicenter
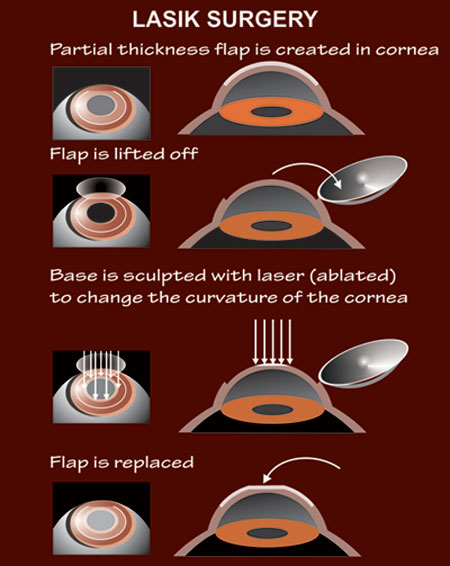
Kadam Eye Lasik Centre Lasik Surgery With Flap Creation

Lasik Complications Epithelial Ingrowth Risk At 50 Endmyopia

Lasik Flap Surl0001 Stock Eye Images

The Lasik Vision Institute Flap Dislocation After Lasik
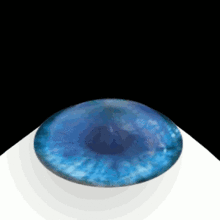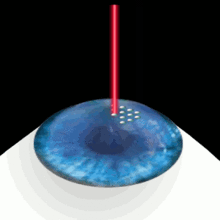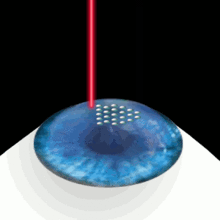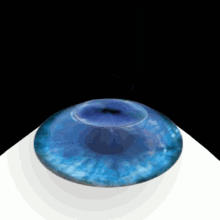
Lasik Wikipedia

Management Of A Traumatic Flap Dislocation Seven Years After Lasik

Prk Vs Lasik Differences Pros Cons And What To Expect

Laser Refractive Surgery Lasik
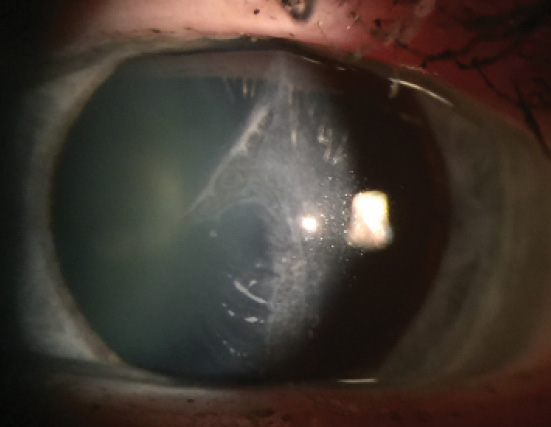
Crstoday Vision Loss After Post Lasik Trauma

Lasik Know The Rewards And The Risks
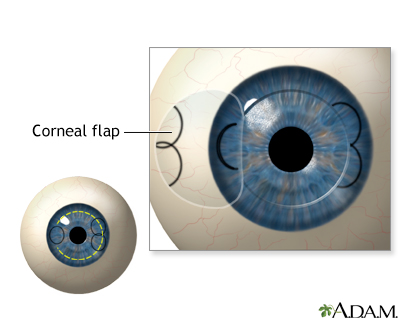
Lasik Eye Surgery Series Procedure Part 2 Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia

Eyeworld Bad Memories Of Flap Complications
Q Tbn And9gctxxqxjjpvvi4xlgrxpldxjizal5f2ir T5evlptk1oe3wovlvu Usqp Cau

Eyeworld Bad Memories Of Flap Complications

Laser Eye Surgery Procedure Laser Eye Surgery Or Lasik Is The Process By Which The Eye S Corneal Flap Is Sliced An Lasik Eye Surgery Lasik Lasik Surgery

Troubleshooting In Lasik Eye News

Traumatic Flap Dislocation 10 Years After Lasik Case Report And Literature Review Sciencedirect

Patients A Guide To Lasik Prk And Smile Tfos Tear Film Ocular Surface Society
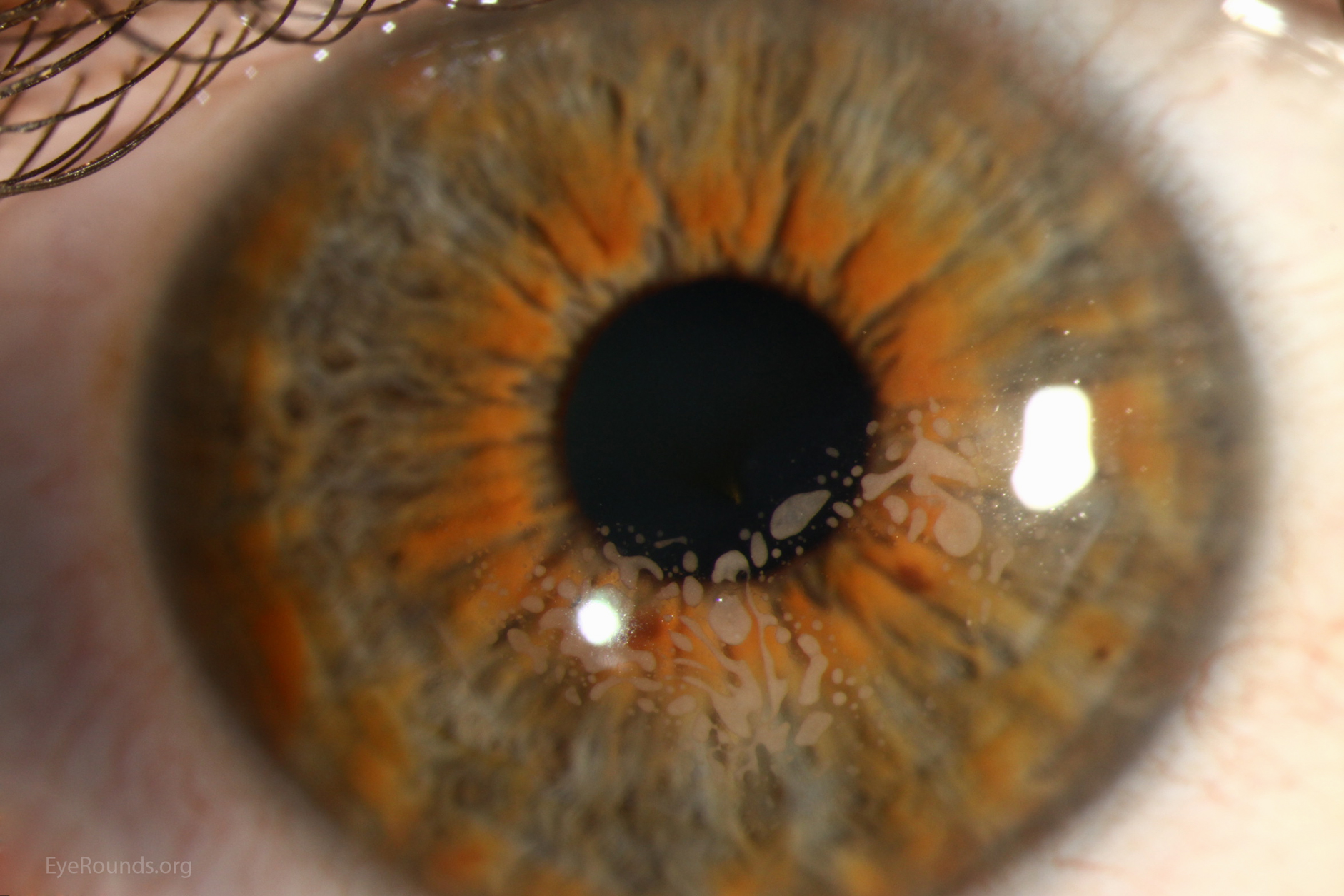
Epithelial Ingrowth Under Lasik Flap
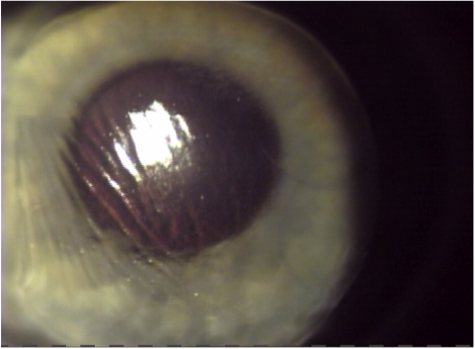
Flap Complications Of Lasik Ask The Eye Doctor Webeyeclinic
Before Enhancing Post Lasik Patients

Femto Lasik Travelmedi

Lasik Complications And Their Management Ento Key

Crsteurope Persistent Lasik Flap Interface Fluid After Dsaek Procedure
Q Tbn And9gcshtyuccybv7vvdxez Ahnisn859qjvndgqzikuakcruwalyzpf Usqp Cau

Case Study Enhancement 13 Years After Lasik Consult Qd

Characterisation Of Corneal Fibrotic Wound Repair At The Lasik Flap Margin British Journal Of Ophthalmology

Lasik Surgery For Thin Cornea Best Options For Patients
Q Tbn And9gcsuqogvtezopkkbaabxhlouhhh4fbcqyb9wrltk7rogroagnb8g Usqp Cau

Lasik Laser Services Gupta Eye Hospital
.jpg)
Lasik Flap Dislocation The Flap Never Heals

Does Corneal Flap Thickness Matter In Lasik
Lasik Thousand Oaks Lasik Surgery Simi Valley Conejo Simi Eye

The Risk Of Flap Complications After Lasik Eye Surgery Maida Customvision

Epithelial Ingrowth Following Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Lasik Prevalence Risk Factors Management And Visual Outcomes Bmj Open Ophthalmology

Lasik Flap Made With Femtosecond Laser Youtube

Lasik Prk

Lasik Interface Primary Complications
Epi Lasik Philadelphia Epi Lasik Bucks County Dr James Lewis
Lasik Eye Videos Eye Consultants Of Pennsylvania
Lasik Eye Surgery Series Aftercare Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia

Hd Corneal Flap Displacement From Eye Trauma After Lasik Em Rap

Best Lasik Eye Surgery Washington Dc Dr Andrew Holzman

Late Post Traumatic Flap Dislocation And Macrostriae After Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Sinha R Shekhar H Tinwala S Gangar A Titiyal Js Oman J Ophthalmol
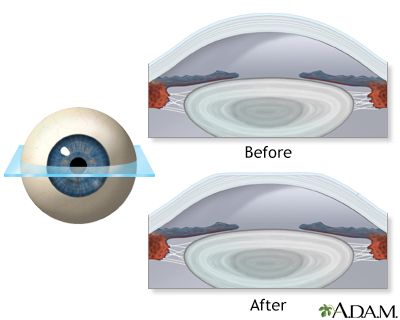
Before Enhancing Post Lasik Patients
Lasik Laser Eye Surgery
Lasik Surgery Recovery Process Wolfe Eye Clinic
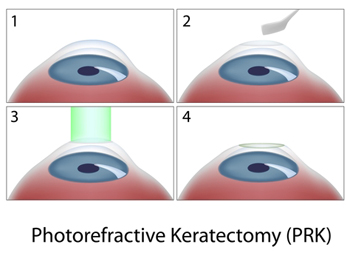
Surface Laser Procedures Alternatives For Lasik Eye Treatment

Lasik Surgery Explained Definition Procedure Results

Full Text Traumatic Corneal Flap Displacement After Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Imcrj

Full Text Traumatic Corneal Flap Displacement After Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Imcrj
My Eye 6 Days After Lasik Eye Surgery Corneal Flap Healing Red Spots Fading Youtube
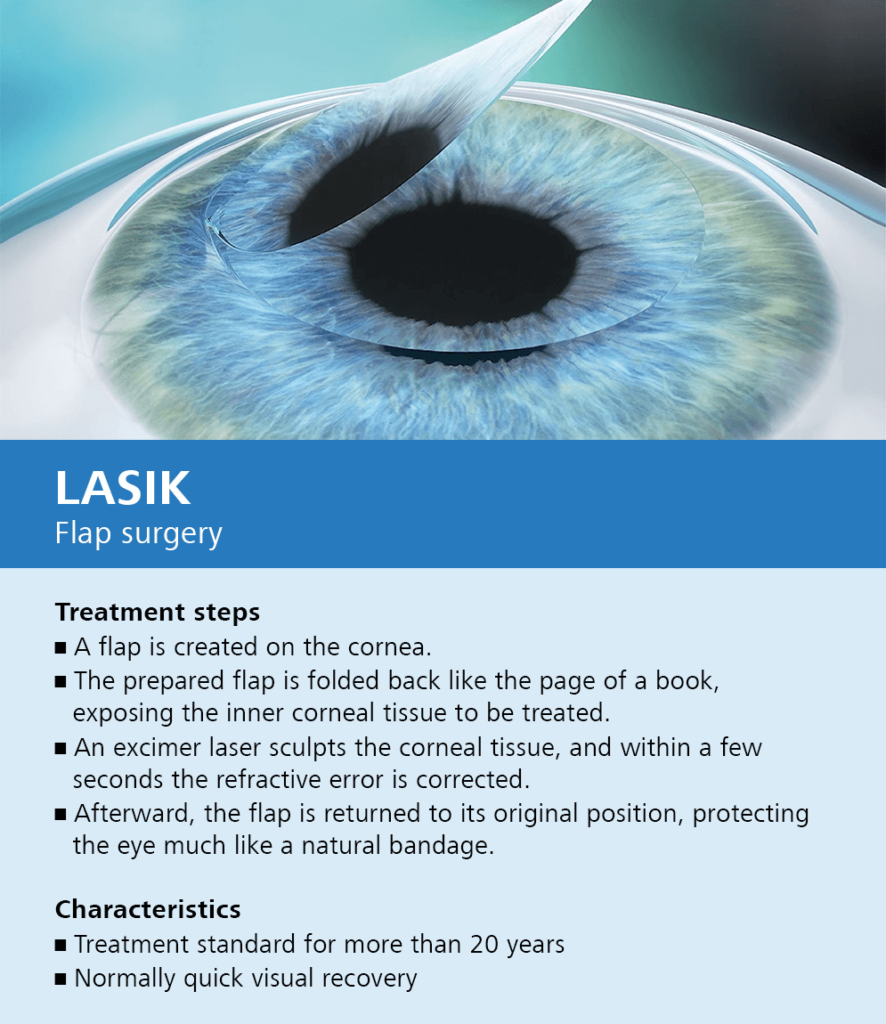
Lasik Beverly Hills Lasik Eye Surgery Beverly Hills Gaster Eye
Laser In Situ Keratomileusis Lasik American Academy Of Ophthalmology
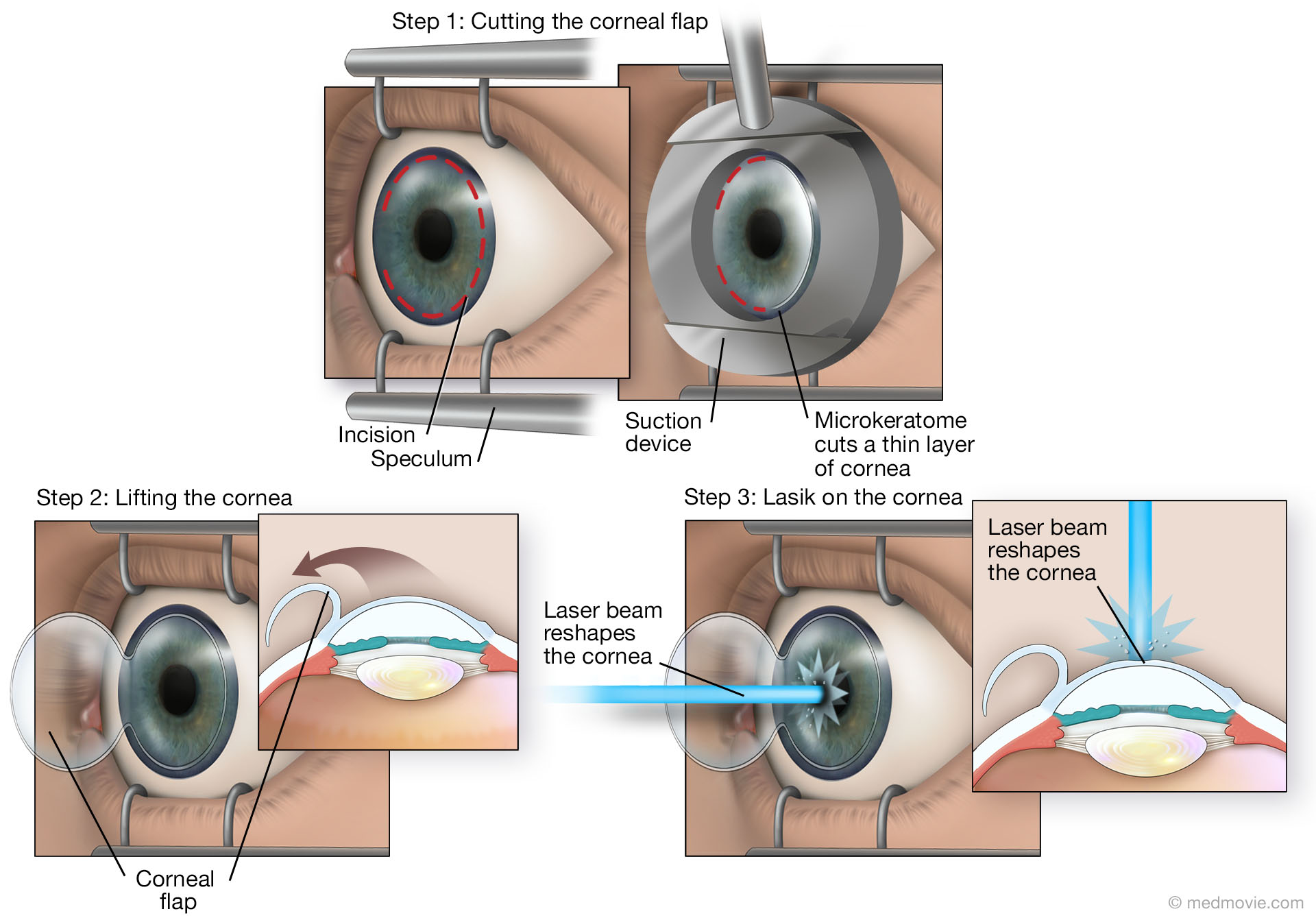
Lasik

Expert Opinion Laser Eye Surgery Gponline

Understanding The Risk Of Lasik And Flap Complications

A Clear Look At The Lasik Flap

Escrs Journal Of Cataract And Refractive Surgery

Bladless Lasik Surgery In Ahmedabad India Eye Care Hospital
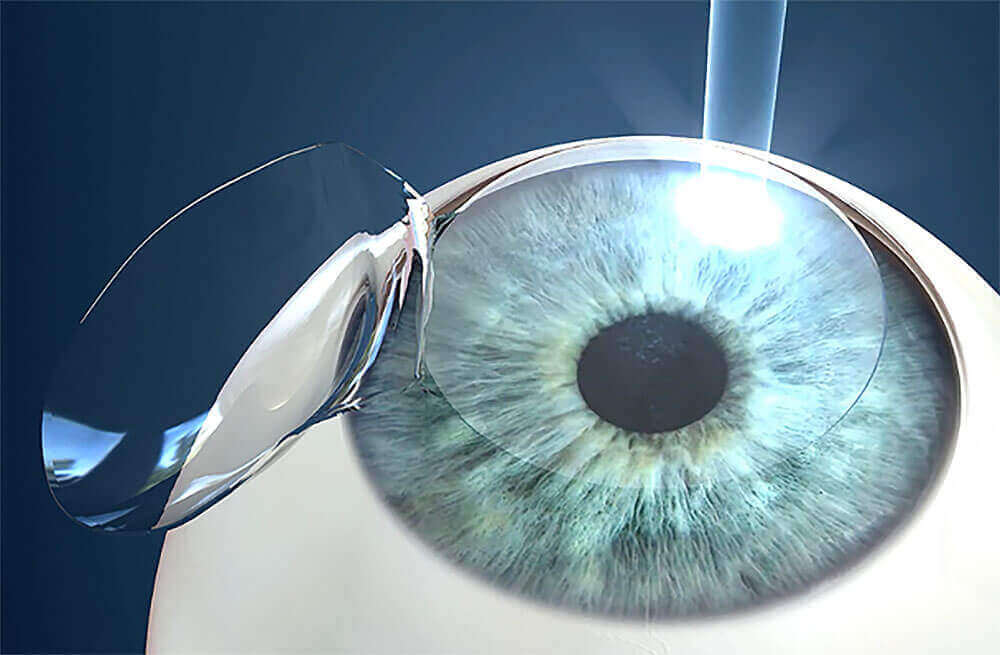
Lasik Center In Boston Ma Laser Vision Correction Boston Laser

Laser Refractive Surgery Lasik Lasek Prk And Ptk Discovery Eye Foundation

Long Term Outcomes Of Flap Amputation After Lasik

Lasik Flap Everything You Need To Know Iq Laser Vision
Q Tbn And9gcq 3vda4gl9aihbd2 Slfkmvh8yfq4ul Loc9hsvxwnwo0v Ld2 Usqp Cau



