Random Priming Method

Performance Comparison Of Reverse Transcriptases For Single Cell Studies Biorxiv

The Double Random Priming Method For Deep Sequencing The First Download Scientific Diagram
Nucleic Acid Probes

Primer Id Validates Template Sampling Depth And Greatly Reduces The Error Rate Of Next Generation Sequencing Of Hiv 1 Genomic Rna Populations Journal Of Virology

Digoxigenin Dig Methods And Kits Sigma Aldrich
Comparison Of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing For Whole Genome Sequencing Of Hantaan Orthohantavirus In Apodemus Agrarius Lung Tissues Scientific Reports
A number of other PCRbased and homologydependent protocols have since been developed which accomplish essentially the same as DNA shuffling, and many of these are summarized in a methods volume 1 Examples include the staggered extension process, 27 randompriming in vitro recombination, 28 and random chimeragenesis on transient templates 29.

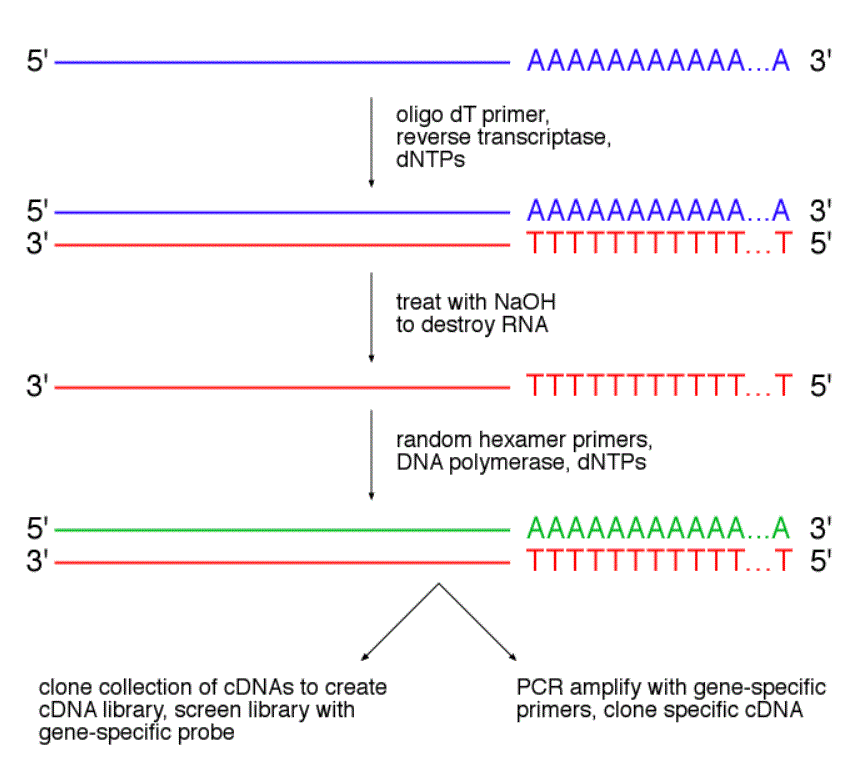
Random priming method. Random Decamers are the same primers currently included in the RETROscript Kit (Cat No AM1710) They are provided at a stock concentration of 50 M, and are functionally tested using the RETROscript KitUsing random primersGenerally, reverse transcription reactions are primed with one of the follow. G of total rna the method relies on a collection of short, computationally selected oligonucleotides, called ‘not sorandom’ (nsr) primers, to obtain fulllength, strandspecific representation of nonribosomal rna transcripts in this study we validated the technique by profiling human whole brain and universal human reference rna using ultrahigh throughput sequencing. DNTP Mix, PCR Grade;.
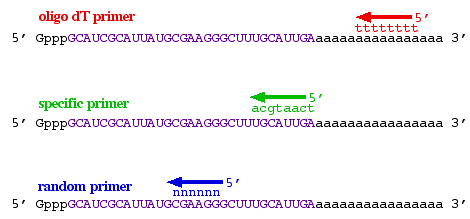
The Random Primer Mix is an optimized mix of hexamer and d(T)23VN primers It provides random priming sites covering the entire RNA templates including both mRNAs and nonpolyadenylated RNAs (such as ribosomal RNAs) The Random Primer Mix yields shorter cDNAs on average and can be used for the detection of multiple short RTPCR products. Used for in situ hybridizations;. The first group of these methods includes approaches based on the use of primers with arbitrary sequence (random priming).
Protocol 1 Random Priming Labeling of Purified DNA Fragments by Extension of Random Oligonucleotides ;. The Random Primers DNA Labeling System is ideal for radioactively labeling DNA, particularly fragments 1 kb The Random Primers DNA Labeling SystemYields 109 cpm/g control DNA using 32 PdCTP25 ng of DNA in one reactionPerformance and Quality Testing Incorporation of a radioactively labeled nu. Sequence 5' d(N6 ) 3' N=A,C,G,T.
Use three different priming methods – random hexamers, anchoredoligo(dT) 18, and sequencespecific primers – depending on the type of analysis needed Contents Transcriptor Reverse Transcriptase;. DNA Shuffling is a very powerful method in which members of a library (ie copies of same gene each with different types of mutation) are randomly shuffled This is done by randomly digesting the library with DNAseI then randomly rejoining the fragments using selfpriming PCR. Random oligonucleotides have been used as primers in a method for labeling DNA to produce high specificactivity probes1,2 The procedure relies on the ability of random hexanucleotides to anneal to multiple sites along the length of a DNA template The primer–template complexes.
Priming #N# What Is Priming?#N# #N#. DNA Shuffling is a very powerful method in which members of a library (ie copies of same gene each with different types of mutation) are randomly shuffled This is done by randomly digesting the library with DNAseI then randomly rejoining the fragments using selfpriming PCR. Anchored Oligo (dT) 18 Primer;.
Protocol 3 Labeling of DNA Probes by Nick Translation ;. The Random Primer Mix is an optimized mix of hexamer and d (T)23VN primers It provides random priming sites covering the entire RNA templates including both mRNAs and nonpolyadenylated RNAs (such as ribosomal RNAs) The Random Primer Mix yields shorter cDNAs on average and can be used for the detection of multiple short RTPCR products. The second method uses random priming Random primers consist of random sequences, frequently of hexamers (6mer) or nonamers (9mer) These are used to prime the RT reaction, leading to the synthesis of cDNA fragments of varying length, which represent the original RNA.
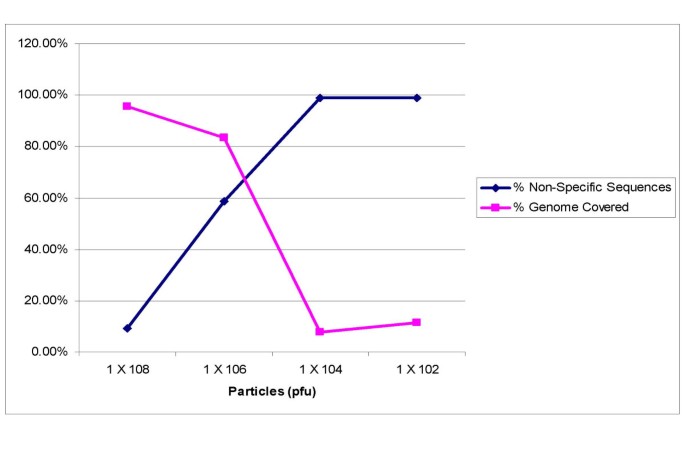
Viral particles are separated from host contaminants using centrifugation and filtration Viral par ticles are treated with DNAse I to remove contaminated nucleic acids Random priming is used to generate 500–1000 bp amplicons which are sizeselected and cloned Colonies are picked and sequenced Sequence is trimmed and assembled. Used for in situ hybridizations;. Use three different priming methods – random hexamers, anchoredoligo(dT) 18, and sequencespecific primers – depending on the type of analysis needed Contents Transcriptor Reverse Transcriptase;.
Genome sequencing by random priming methods for viral identification Rosseel Toon Dissertation submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Veterinary Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, 15 Promotors Dr Steven Van Borm Prof Dr Hans Nauwynck. Used to screen gene libraries;. The Random Primer Mix is an optimized mix of hexamer and d (T)23VN primers It provides random priming sites covering the entire RNA templates including both mRNAs and nonpolyadenylated RNAs (such as ribosomal RNAs) The Random Primer Mix yields shorter cDNAs on average and can be used for the detection of multiple short RTPCR products.
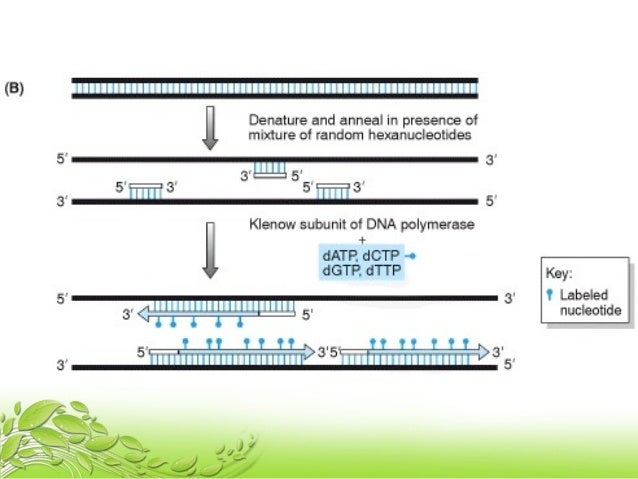
Random primed labeling developed by Feinberg and Vogelstein (1, 2) solves all of these problems The technique uses short random sequence hexanucleotides (in the original method) which prime the denatured target DNA at numerous sites The Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I is then used to synthesize new strands of DNA from these primed sites. Random Primer 6 is a mixture of random hexanucleotides is used to prime DNA synthesis in vitro along multiple sites of denatured template DNA;. Priming Priming is the method of continually taking a substance over a number of days to get (better) effects from it Many legal herbs are subject to this effect.
Random Primer 6 is a mixture of random hexanucleotides is used to prime DNA synthesis in vitro along multiple sites of denatured template DNA;. 1 A molecule, which may be a small polymer, that initiates the synthesis of a larger structure Synonym(s) starter. This RNA library preparation method takes total purified RNA as input and enriches for polyadenylated (polyA) transcripts using oligodT coated beads PolyA RNA is subsequently fragmented using heat and Mg and reverse transcribed into cDNA using random priming Illiumina adapters are ligated to dsDNA and PCR amplified.
Priming is a technique whereby exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus, without conscious guidance or intention For example, the word NURSE is recognized more quickly following the word DOCTOR than following the word BREAD Priming can be perceptual, semantic, or conceptual Research, however, has yet to firmly establish the duration of priming effects, yet their onset can be almost instantaneous Priming works best when the two stimuli are in the same modality. Protocol 4 Labeling of DNA Probes by Polymerase Chain Reaction. If reward priming reflects increased salience of recently rewarded features, the effect should be replicable in any paradigm where there is sufficient selection pressure, and the random feature (eg, color) is sufficiently salient We therefore expected to find results consistent with 1trial reward priming in our conceptually identical paradigm.
Nonuniform random priming caused noncontinuous length distribution in the final sequencing products When the final sequencing data was sorted to 150–0 bp, 0–300 bp, 300–500 bp and 150–500 bp size fractions, it was found that the selection of size fraction affected the outcome, the relative abundance of species ( Supplementary. Used to probe northern and southern blots;. Used to probe northern and southern blots;.
Random priming (14) Poly(A)selected RNA like an isolated mRNA fraction or amplified RNA (aRNA) are preferably reverse transcribed with random primers, because random priming is less likely to give a 3′ end bias in the resulting cDNA Here we report a novel priming method for reverse transcription reactions and a study of the implication. Genome sequencing by random priming methods for viral identification Rosseel Toon Dissertation submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Veterinary Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, 15 Promotors Dr Steven Van Borm Prof Dr Hans Nauwynck. Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods Djikeng A(1), Halpin R, Kuzmickas R, Depasse J, Feldblyum J, Sengamalay N, Afonso C, Zhang X, Anderson NG, Ghedin E, Spiro DJ using viral preparations from cell culture supernatant, allantoic fluid and fecal matter CONCLUSION The method described is of great utility in generating whole.
The method involves priming template polynucleotide(s) with randomsequence primers and extending to generate a pool of short DNA fragments which contain a controllable level of point mutations The fragments are reassembled during cycles of denaturation, annealing and further enzymecatalyzed DNA polymerization to produce a library of fulllength sequences. Synonyms for random primer method in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for random primer method 11 synonyms for primer fuze, fuse, priming, fuzee, fusee, flat coat, primer coat, priming coat, undercoat, priming, ground What are synonyms for random primer method?. Used to screen gene libraries;.
Transcriptor RT Reaction Buffer, 5x concentrated;. 1 A statisticallybased randompriming method for determining nucleotide sequence in a nucleic acid template having a completely unknown or partly known nucleotide sequence by priming within a region of the template for which the nucleotide sequence is not known, the method comprising the steps of. 1 A statisticallybased randompriming method for determining nucleotide sequence in a nucleic acid template having a completely unknown or partly known nucleotide sequence by priming within a region of the template for which the nucleotide sequence is not known, the method comprising the steps of.
Anchored Oligo (dT) 18 Primer;. The major benefits to random priming are the production of shorter cDNA fragments and increasing the probability that 5' ends of the mRNA would be converted to cDNA. Protocol 2 Random Priming Labeling of DNA by Extension of Random Oligonucleotides in the Presence of Melted Agarose ;.
Ensures the presence of virtually all sequence combination of hexamer primers;. A method of priming and drying substrates having highaspect ratio trenches L'invention porte sur un procédé d'apprêtage et de séchage de substrats ayant des sillons à rapport de forme élevé This process is referred to herein as 'priming' Ce procédé est ici appelé 'apprêtage'. Transcriptor RT Reaction Buffer, 5x concentrated;.
OligodT is used to prime approximately 40% of realtime RTPCR assays It is more specific than random priming, and is the best method to use when the aim is to obtain a faithful cDNA representation of the mRNA pool It is also the most appropriate choice when aiming to amplify several target mRNAs from a limited RNA sample. Random priming is incapable of distinguishing between mRNA and other RNA species present in the reaction Primer Sequence 5´ – d (NNNNNN) –3´ N = G, A, T or C A mixture of random hexamer primers and oligo(dT) may improve the sensitivity of cDNA synthesis. Viral particles are separated from host contaminants using centrifugation and filtration Viral particles are treated with DNAse I to remove contaminated nucleic acids Random priming is used to generate 500–1000 bp amplicons which are sizeselected and cloned Colonies are picked and sequenced Sequence is trimmed and assembled.
Synonyms for random primer method in Free Thesaurus Antonyms for random primer method 11 synonyms for primer fuze, fuse, priming, fuzee, fusee, flat coat, primer coat, priming coat, undercoat, priming, ground. A mixture of random primers and oligo dT works in all situations Oligo dT priming works in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but gives one 3' bias (thus primers for PCR/qPCR are best designed near. The first group of these methods includes approaches based on the use of primers with arbitrary sequence (random priming) Another group of methods to detect DNA polymorphism is based on the use of primers that consist of short repetitive sequences having anchor nucleotides at the 5' or 3'ends that position the annealing sites of these primers (microsatellite priming).
Sequence 5' d(N6 ) 3' N=A,C,G,T. Genome sequencing by random priming methods for viral identification Rosseel Toon Dissertation submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Veterinary Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Ghent University, 15 Promotors Dr Steven Van Borm Prof Dr Hans Nauwynck. Steps for learning the details of QPCR methods, how to use these methods effectively, and the most appropriate analysis techniques to provide reliable and reproducible results The guide starts with a brief introduction to QPCR and experimental design This is perhaps the most crucial step in the QPCR process as it lays the.
Abstract Here we report a new methodology to study trace amounts of DNA of unknown sequence using a twostep PCR strategy to amplify and clone target DNA The first PCR is carried out with a partial random primer comprised of a specific 21nucleotide 5′ sequence, a random heptamer, and a 3′ TGGC clamp The second PCR is carried out with a single 19nucleotide primer that matches the specific 5′ sequence of the partial random primer. Ensures the presence of virtually all sequence combination of hexamer primers;. Random primed labeling, based on the method of Feinberg and Vogelstein (1) is a method of incorporating radioactive nucleotides along the length of a fragment of DNA Random primed labeling can give specific activities of between 2 × 10 (9) and 5 × 10 (9) dpm/μg (see Note 1) The following method is essentially that described by Feinberg and Vogelstein (2) in which a DNA fragment is denatured by heating in a boiling water bath.
1 Priming with oligo(dT) by itself is decidedly better at producing larger cDNA inserts 2 Random hexamer priming yields cDNA that are smaller on average but that may better represent the entire RNA template Priming with random hexamers at a concentration of 50–150 ng per reaction generally yields twice the amount. The method described is of great utility in generating whole genome assemblies for viruses with little or no available sequence information, viruses from greatly divergent families, previously uncharacterized viruses, or to more fully describe mixed viral infections Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods BMC Genomics 08 Jan 7. The SMA method (Fig 1B) uses oligonucleotides (SMAp1) with random 3′ sequences for capture of the whole cDNA sequence and a universal 5′ sequence that serves as a priming site for uniform PCR amplification of all cDNA fragmentsThe cDNA before SMA remained intact, but the method produced similar results if the cDNA was fragmented into short pieces.
Although random priming can amplify an unknown target, it often yields lower amounts of DNA than specific primers, which can reduce the overall sensitivity of the process Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) using bacteriophage phi29 polymerase with random primers allows DNA synthesis in amounts compatible with the downstream use of DNA microarrays Moreover, MDA has the potential to amplify the whole DNA genome (whole genome amplification, WGA) of target pathogens in the presence of. Priming is a psychological process in which exposure to a stimulus activates a concept in memory that is then given increased weight in subsequent judgment tasks Priming works by making the activated concept accessible so that it can be readily used in evaluating related objects. The first PCR is carried out with a partial random primer comprised of a specific 21nucleotide 5′ sequence, a random heptamer, and a 3′ TGGC clamp The second PCR is carried out with a single 19nucleotide primer that matches the specific 5′ sequence of the partial random primer.
Place a small amount of glass wool at the bottom of a 1 mL syringe Load sephadex G50 (saturated inTE pH 74, 02% SDS) into the 1 mL syringe Pack the minicolumn by spinning the 1 mL syringe in a 15 mL conical tube in a clinical centrifuge on a setting of 6 for 30 seconds. The SMA method (Fig 1B) uses oligonucleotides (SMAp1) with random 3′ sequences for capture of the whole cDNA sequence and a universal 5′ sequence that serves as a priming site for uniform PCR amplification of all cDNA fragments The cDNA before SMA remained intact, but the method produced similar results if the cDNA was fragmented into short pieces. This in vitro homologous recombination method begins with the synthesis of many short gene fragments exhibiting point mutations using random sequence primers These fragments are reassembled to full length parental genes using primerless PCR.
Viral genome sequencing by random priming methods Appolinaire Djikeng, 1 Rebecca Halpin, 1 Ryan Kuzmickas, 1 Jay DePasse, 5 Jeremy Feldblyum, 1 Naomi Sengamalay, 1 Claudio Afonso, 2 Xinsheng Zhang, 3 Norman G Anderson, 4 Elodie Ghedin, 5 and David J Spiro 1 Author information. OligodT is used to prime approximately 40% of realtime RTPCR assays It is more specific than random priming, and is the best method to use when the aim is to obtain a faithful cDNA representation of the mRNA pool It is also the most appropriate choice when aiming to amplify several target mRNAs from a limited RNA sample. DNTP Mix, PCR Grade;.

A Nonspecific Primer Anchored Pcr Technique For Chromosome Walking

Digoxigenin Dig Methods And Kits Sigma Aldrich

Primer Selection Guide For Use With Goscript Reverse Transcription Mixes
Evaluation Of Bias Induced By Viral Enrichment And Random Amplification Protocols In Metagenomic Surveys Of Saliva Dna Viruses Microbiome Full Text
Cdna Random Hexamer Department Of Molecular Genetics

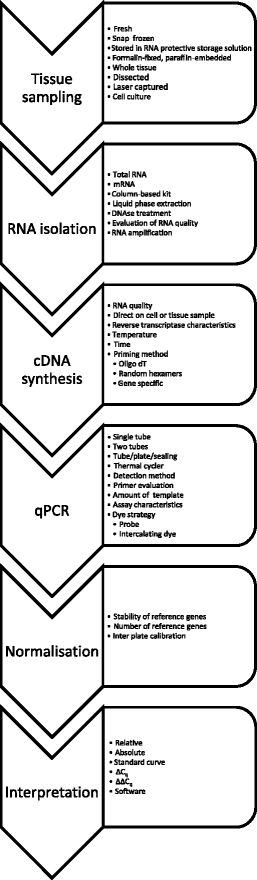
Gene Quantification Optimisation Real Time Kinetic Pcr Rt Pcr Reactions

Determination Of Density Required For Digital Transcriptome Analysis Application To An Androgen Sensitive Prostate Cancer Model Pnas
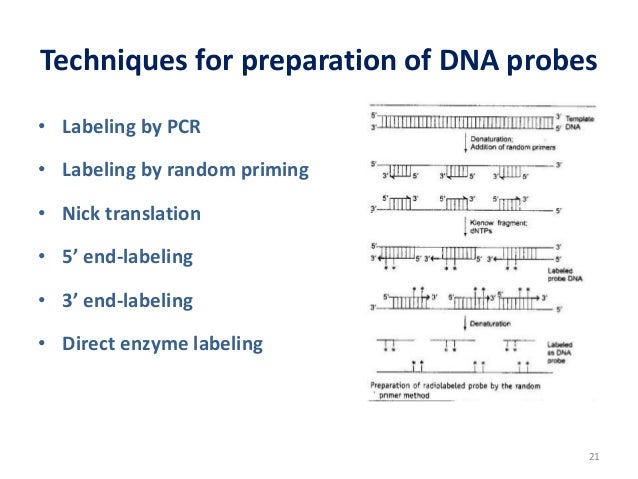
Lectut Btn 2 Ppt L23 Labeling Techniques For Nucleic Acids

The Double Random Priming Method For Deep Sequencing The First Download Scientific Diagram
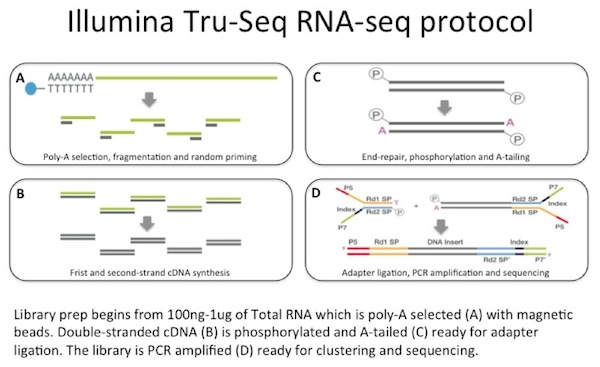
An Introduction To Rna Seq
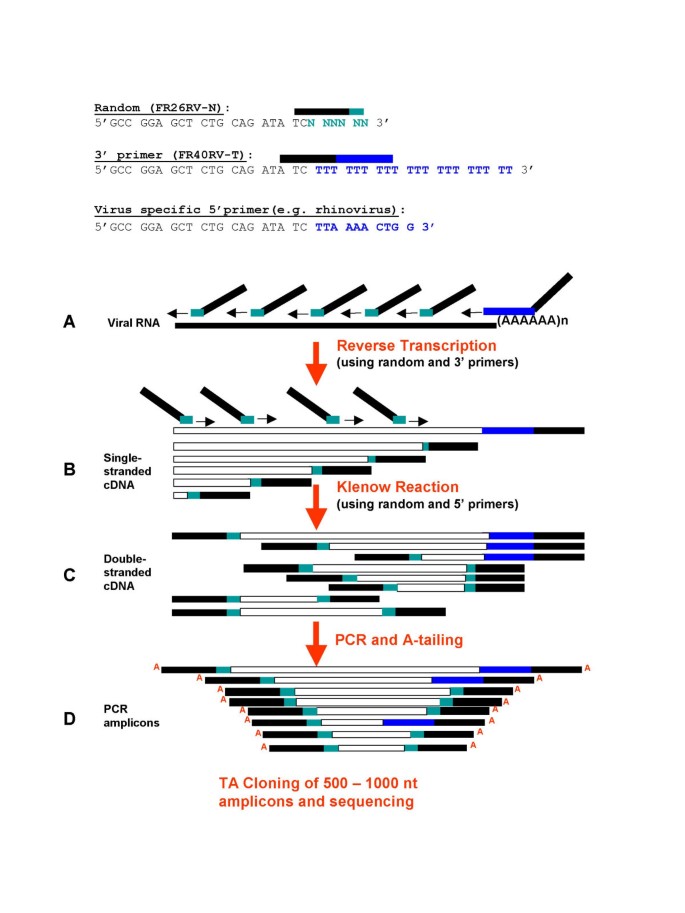
Viral Genome Sequencing By Random Priming Methods Bmc Genomics Full Text
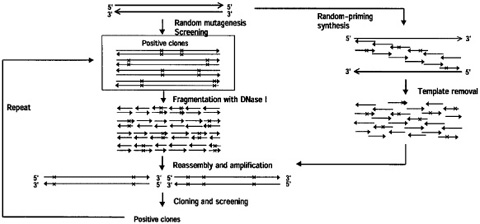
Dna Shuffling And Family Shuffling For In Vitro Gene Evolution Springerlink

Basic Principles Of Rt Qpcr Thermo Fisher Scientific Us
Quantification Of Gpcr Mrna Using Real Time Rt Pcr Springerlink

Random Primer Mix Neb

Pdf Viral Genome Sequencing By Random Priming Methods

Pcr Overview Goldbio
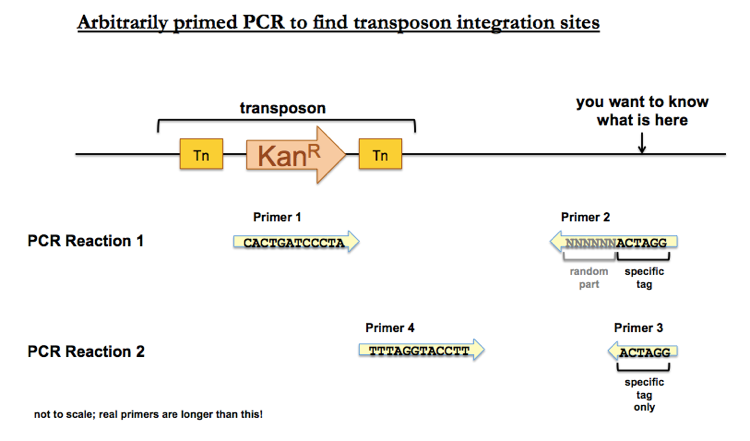
Genetics 11 Transposon Sequencing Tn Seq How To Identify Mutants That Die
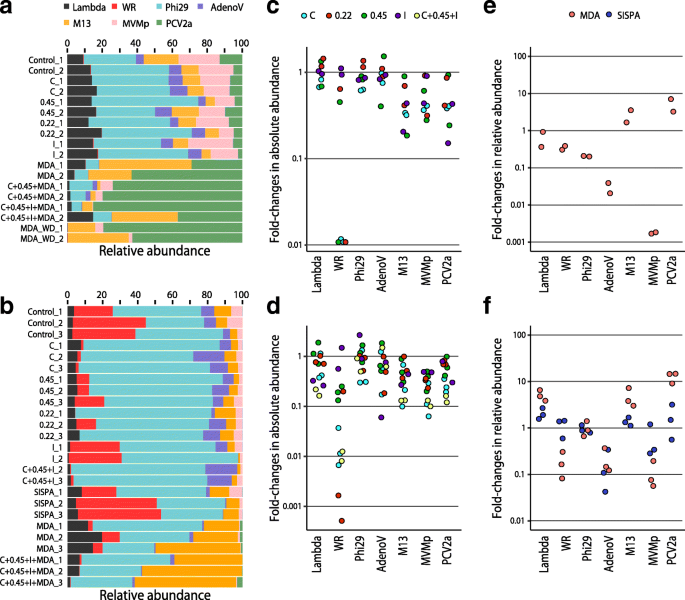
Evaluation Of Bias Induced By Viral Enrichment And Random Amplification Protocols In Metagenomic Surveys Of Saliva Dna Viruses Microbiome Full Text
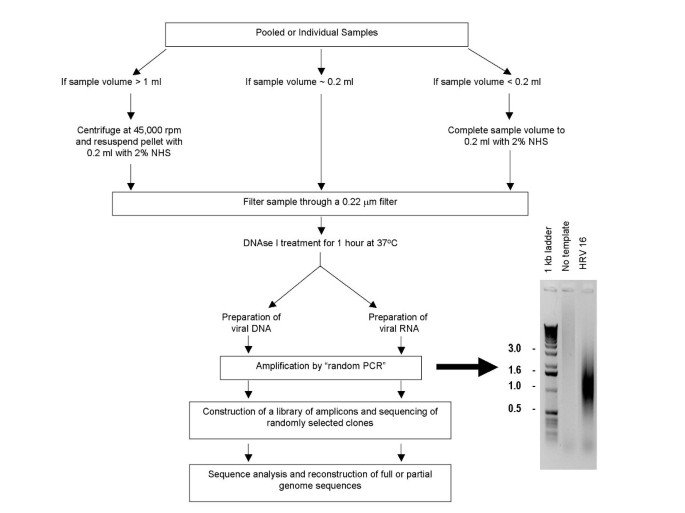
Viral Genome Sequencing By Random Priming Methods Bmc Genomics Full Text

Transcriptor First Strand Cdna Synthesis Kit

The Future Of Dna Amplification Cytiva Formerly Ge Healthcare Life Sciences
What Are The Differences Between Dna And Rna Probes Enzo Life Sciences

A Method To Convert Mrna Into A Grna Library For Crispr Cas9 Editing Of Any Organism Science Advances

Primer Dna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

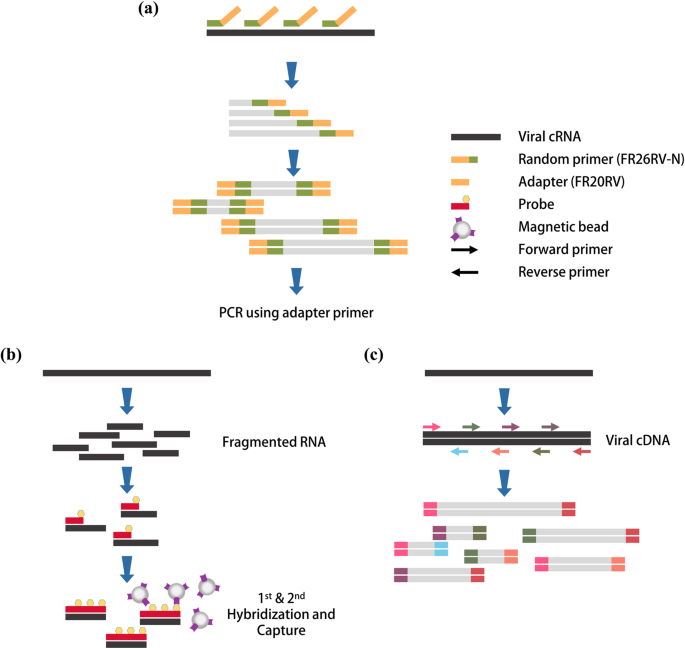
A Universal Next Generation Sequencing Protocol To Generate Noninfectious Barcoded Cdna Libraries From High Containment Rna Viruses Msystems

Pdf In Vitro Dna Recombination By Random Priming Semantic Scholar
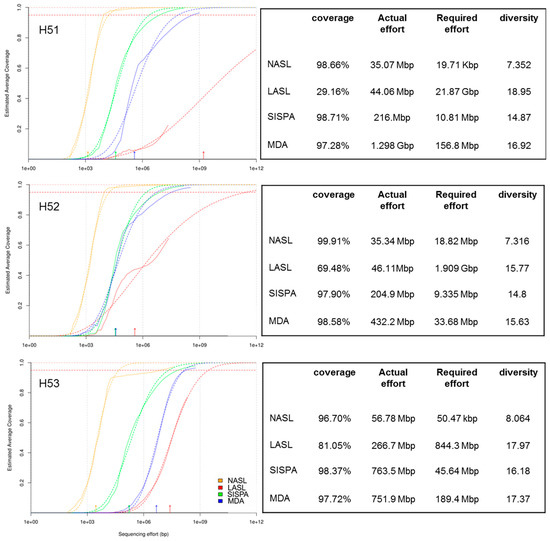
Viruses Free Full Text Evaluation Of Sequencing Library Preparation Protocols For Viral Metagenomic Analysis From Pristine Aquifer Groundwaters Html
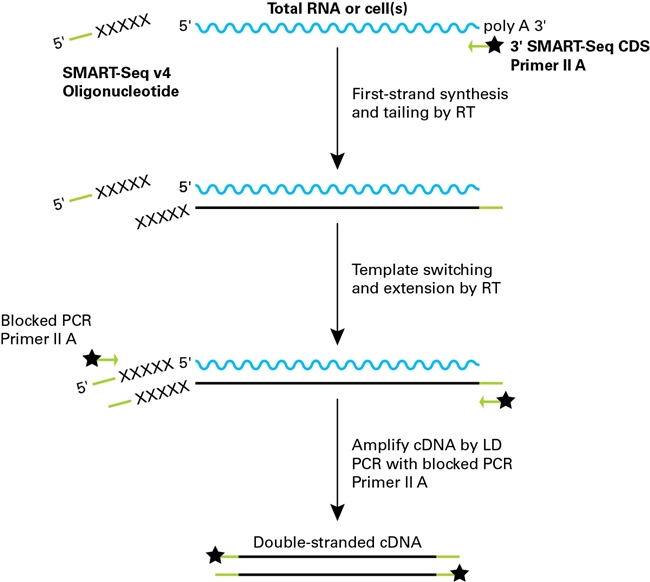
Smart Technology Overview

Bioprime Array Cgh Genomic Labeling System
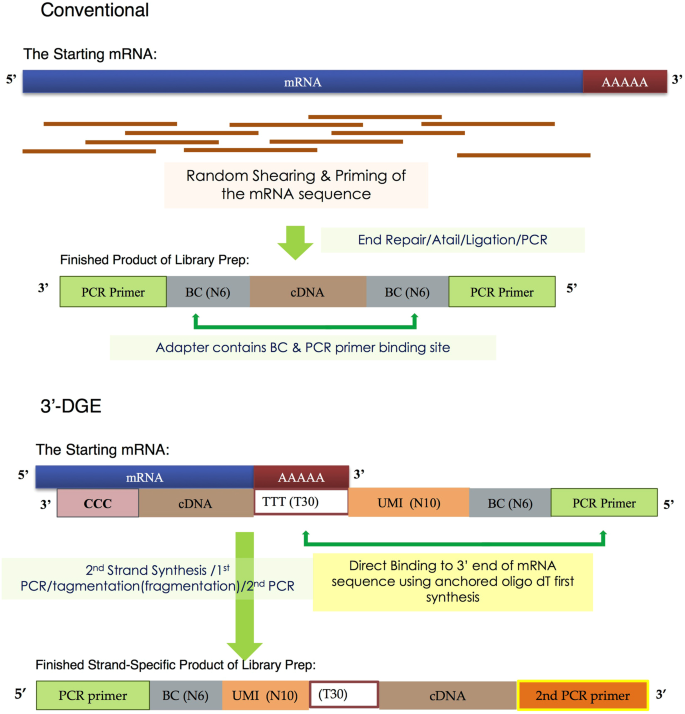
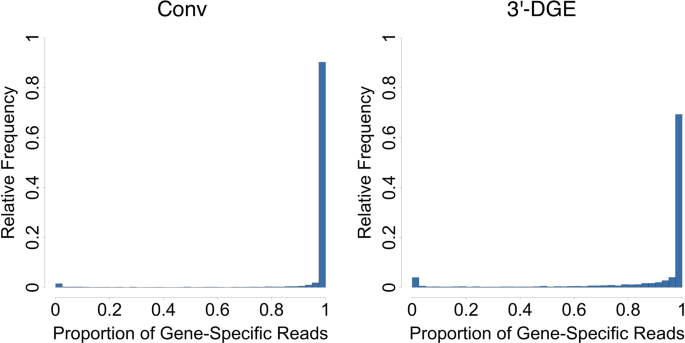
A Comparison Of Mrna Sequencing With Random Primed And 3 Directed Libraries Scientific Reports

Primer Dimer Wikipedia
Viral Genome Sequencing By Random Priming Methods Bmc Genomics Full Text
A Comparison Of Mrna Sequencing With Random Primed And 3 Directed Libraries Scientific Reports

Primer Selection Guide For Use With Goscript Reverse Transcription Mixes

ged Random Hexamer Amplification Trha Strategy Download Scientific Diagram

Reverse Transcription Technology

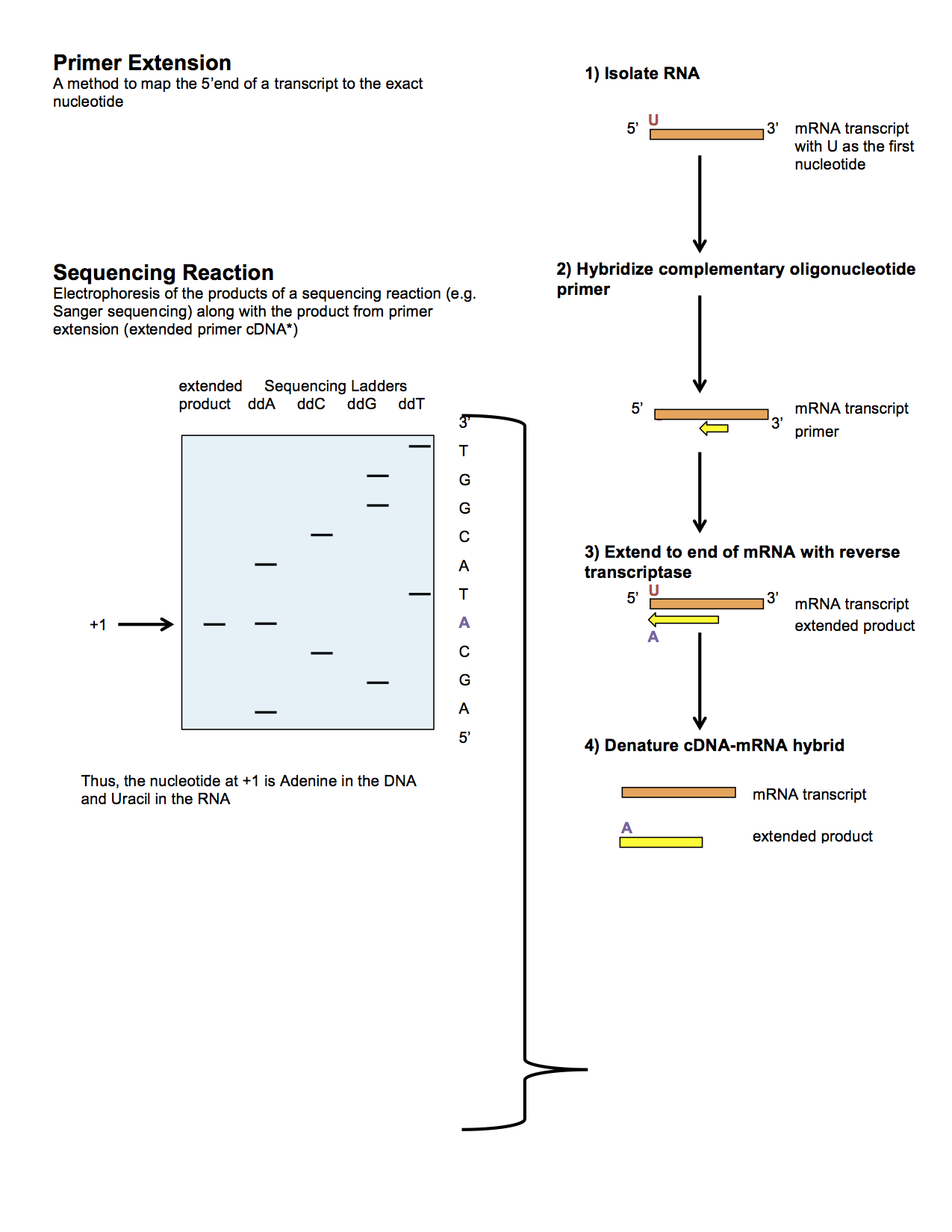
Primer Extension Wikipedia

Reverse Transcription Pcr Principle Procedure Application Advantages And Disadvantages

Metagenomic Sequencing With Spiked Primer Enrichment For Viral Diagnostics And Genomic Surveillance Nature Microbiology
Cdna Production
Use Of Labeled Primers For Differential Display Unt Digital Library

Usa1 Methods And Kits For Sense Rna Synthesis Google Patents
Plos One Characterization Of Rna From Exosomes And Other Extracellular Vesicles Isolated By A Novel Spin Column Based Method
Primer Extension Wikipedia

Pcr Rt Abm Inc

Rna Seqlopedia

Pcr Overview Goldbio

Approach To Molecular Characterization Of Partially And Completely Untyped Samples In An Indian Rotavirus Surveillance Program Sciencedirect

Nick Translation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Random Primers Or Oligo Dt Primers For Cdna Synthesis
Single Primer Isothermal Amplification Spia Combined With Next Generation Sequencing Provides Complete Bovine Coronavirus Genome Coverage And Higher Sequence Depth Compared To Sequence Independent Single Primer Amplification Sispa

Random Amplified Polymorphic Dna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna And Rna Labeling Radiolabeled Nucleotides
Random Priming In Vitro Recombination Rpr I Synthesis Of Short Download Scientific Diagram

Targeted Reduction Of Highly Abundant Transcripts Using Pseudo Random Primers Biotechniques

Schematic Outline Of The Vana Based Metagenomics Method Top Left Download Scientific Diagram

Two Methods For Full Length Rna Sequencing For Low Quantities Of Cells And Single Cells Pnas

Digoxigenin Dig Methods And Kits Sigma Aldrich

Nick Translation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Basic Principles Of Rt Qpcr Thermo Fisher Scientific Us

Pdf Viral Genome Sequencing By Random Priming Methods

Oligo Dt Primer Generates A High Frequency Of Truncated Cdnas Through Internal Poly A Priming During Reverse Transcription Pnas
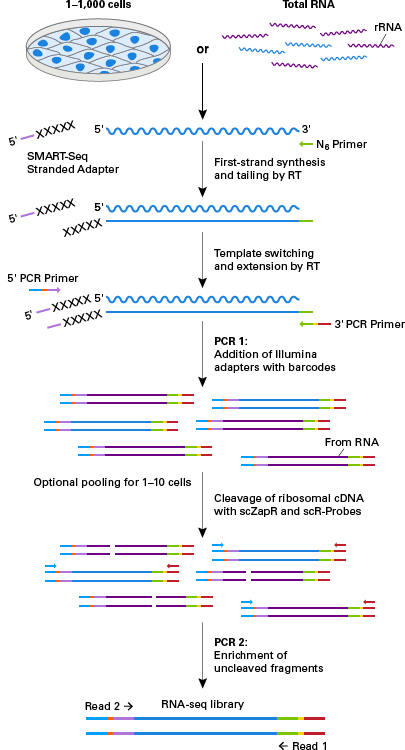
Full Transcriptome Analysis Of Single Cells With The Smart Seq Stranded Kit
Reverse Transcription Pcr Technologies Guide Sigma Aldrich
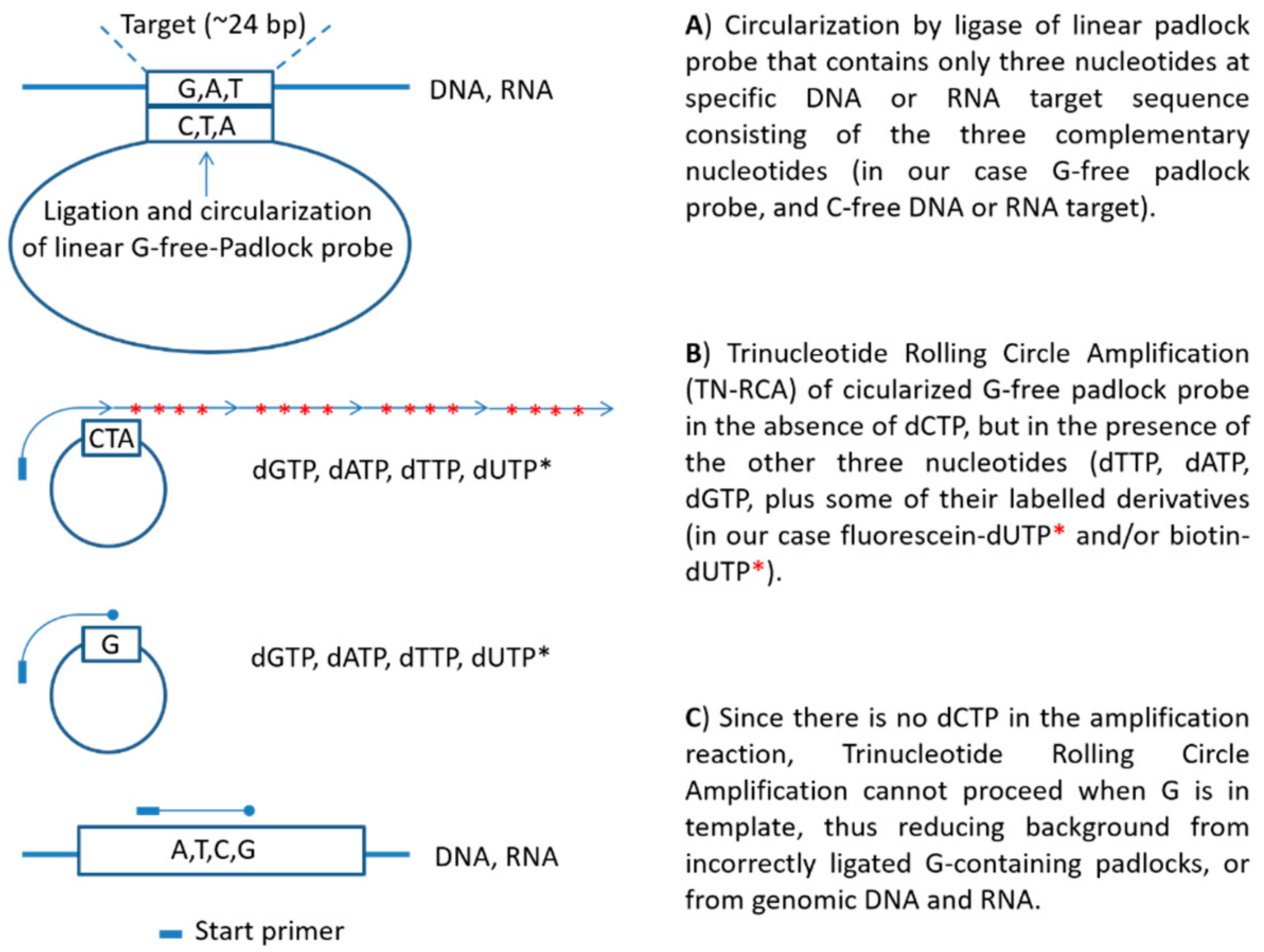
Mps Free Full Text Trinucleotide Rolling Circle Amplification A Novel Method For The Detection Of Rna And Dna Html

Pcr Amplification An Introduction To Pcr Methods Promega
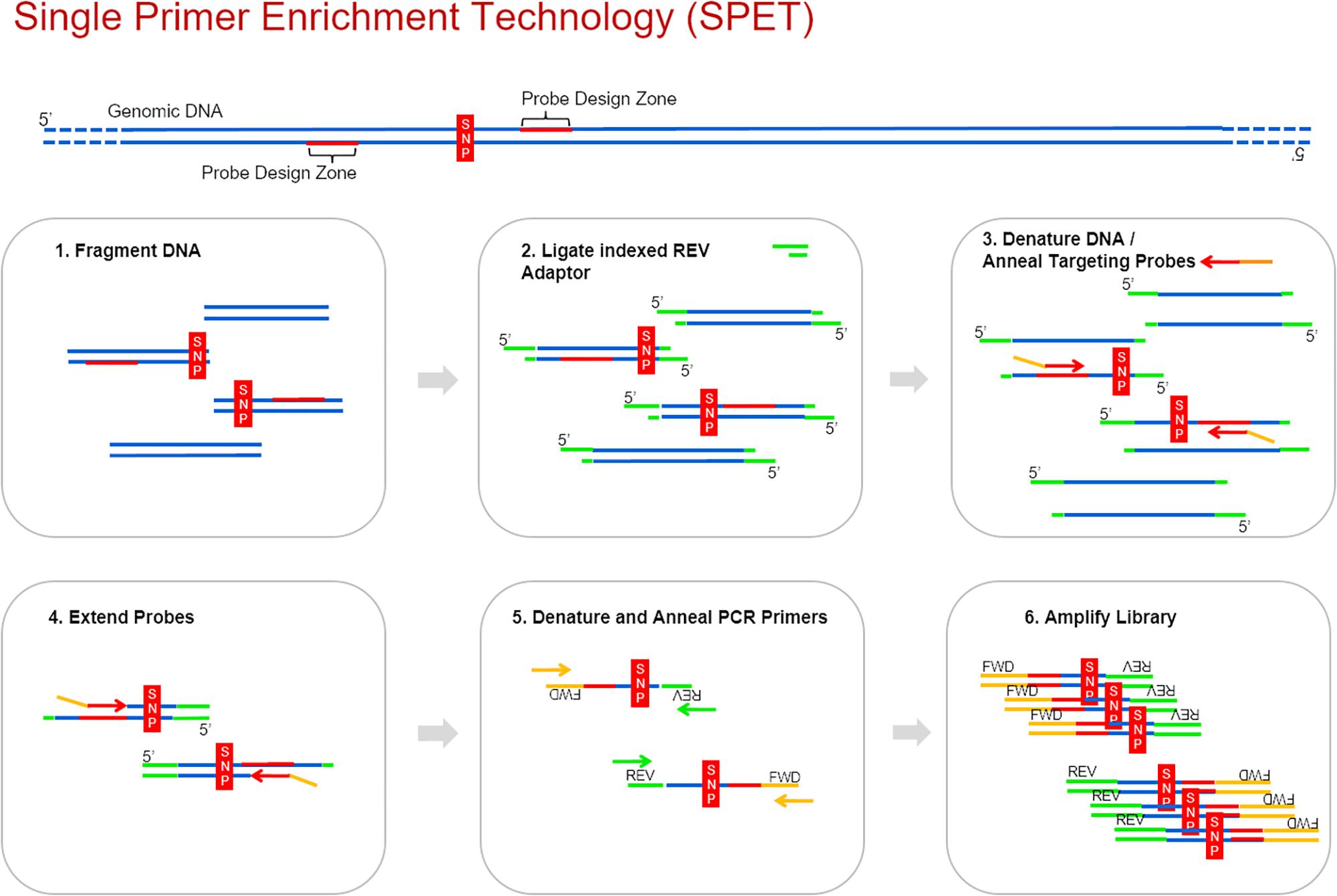
Frontiers Single Primer Enrichment Technology Spet For High Throughput Genotyping In Tomato And Eggplant Germplasm Plant Science
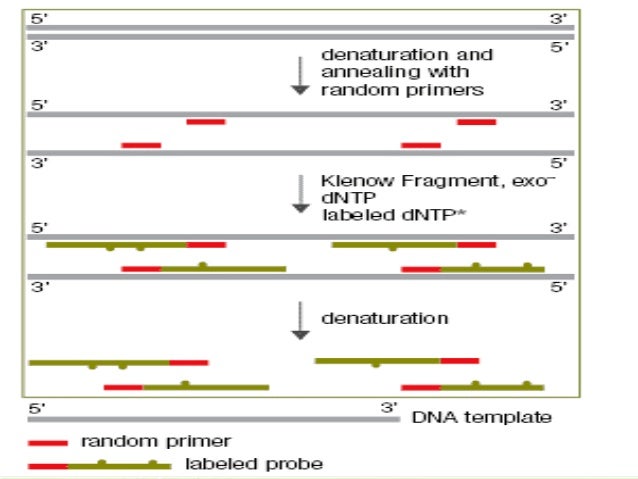
Nucleic Acid Probes

A Broadly Applicable Coi Primer Pair And An Efficient Single Tube Amplicon Library Preparation Protocol For Metabarcoding Rennstam Rubbmark 18 Ecology And Evolution Wiley Online Library

Reverse Transcription Pcr Principle Procedure Application Advantages And Disadvantages

Final Exam Flashcards Quizlet

Difference Between Nick Translation And Primer Extension Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Performance Comparison Of Reverse Transcriptases For Single Cell Studies Biorxiv

Nucleic Acid Hybridization Nucleic Acid Hybridization Is A Fundamental Tool In Molecular Genetics Which Takes Advantage Of The Ability Of Individual Single Stranded Ppt Download
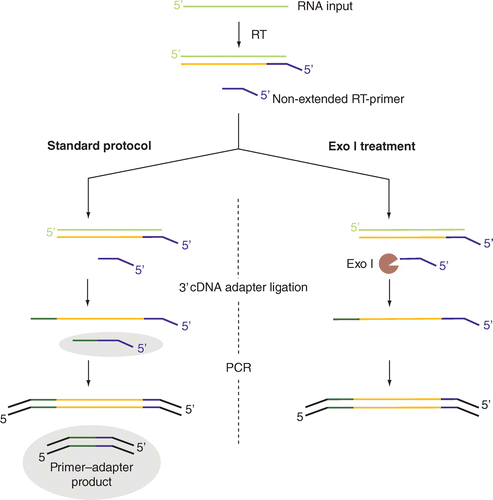
Excess Primer Degradation By Exo I Improves The Preparation Of 3 Cdna Ligation Based Sequencing Libraries Biotechniques

Reverse Transcription Pcr Technologies Guide Sigma Aldrich
How Are Radioactive Probes Produced Quora

Figure 3 From Tardis A Targeted Rna Directional Sequencing Method For Rare Rna Discovery Semantic Scholar

Dna Strands Can Be Separated Under Conditions Which Break H Bonds Ppt Video Online Download
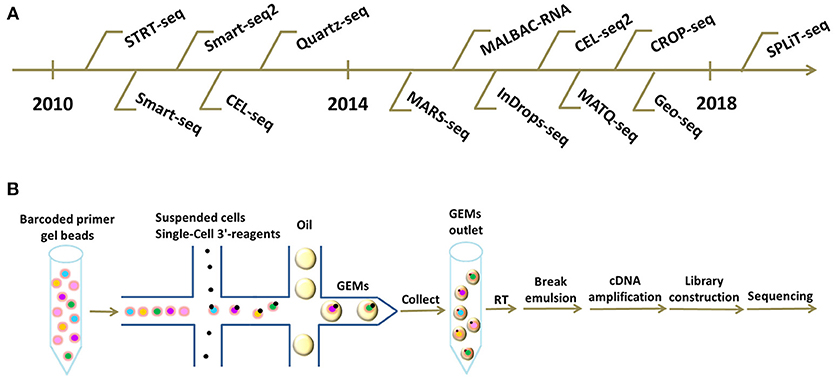
Frontiers Technical Advances In Single Cell Rna Sequencing And Applications In Normal And Malignant Hematopoiesis Oncology

Pre Amplification Scheme 1 First Strand Cdna Synthesis Is Primed Download Scientific Diagram

Use Of Sequence Independent Single Primer Amplification Sispa For Rapid Detection Identification And Characterization Of Avian Rna Viruses Sciencedirect
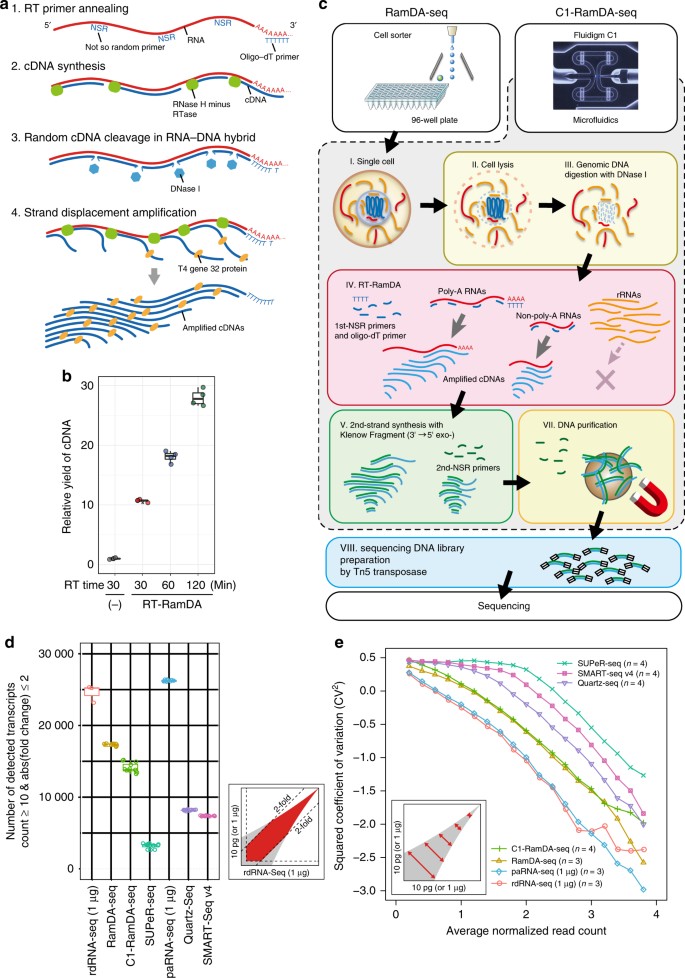
Single Cell Full Length Total Rna Sequencing Uncovers Dynamics Of Recursive Splicing And Enhancer Rnas Nature Communications



